A Faculty Reborn
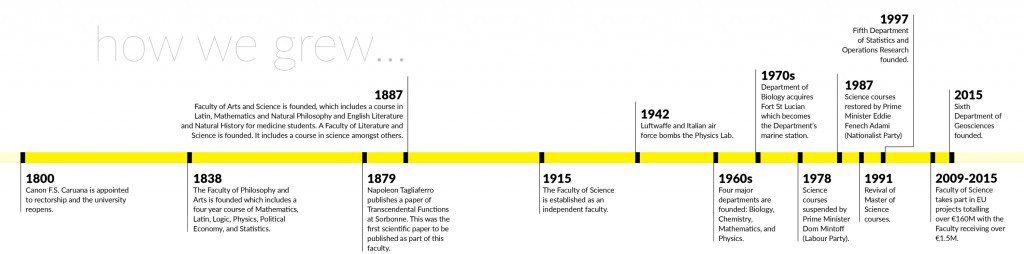
During the mid-1970s, the Faculties of Science and Arts were closed down, and the Bachelor programmes phased out. Most of the foreign (mainly British) academics left Malta, as did some Maltese colleagues. Those few who stayed were assigned teaching duties at the newly established Faculty of Education and Faculty of Engineering. Relatively little research took place, except when funds were unneccessary, and it is thanks to these few that scientific publications kept trickling out.
In 1987, the Faculties of Arts and Science were reconstituted. The Faculty of Science had four ‘divisions’ which became the Departments of Biology, Chemistry, Physics, and Mathematics. In the same year, I returned from the UK to join the Faculty.
Things gradually improved as more staff and students joined. However, equipment was either obsolete or beyond repair. The B.Sc. (Bachelor of Science) course was re-launched with an evening course. Faculty members worked flat out in very poor conditions. The Physics and Mathematics building was still shared with Engineering. Despite these problems, we had a Faculty and identity. Nevertheless, we wanted our courses to be of international repute—our guiding principle.
During the 1990s, yearly budgets had improved slightly along with experimental facilities. Computers and the occasional capital investment helped immensely. Research output increased, as did student numbers, while postgraduate Masters and Ph.D. students started to appear.
Since 2005, some faculty members have been working hard to secure European Regional Development Funds (ERDF) by submitting proposals to reinforce our research infrastructure. A total of six projects were approved with a combined budget of nearly €5 million. This has resulted in new, state of the art research facilities and an exponential increase in research output, bolstered by additional academic staff and research student numbers of close to 80.
Students are now organised and active through S-Cubed, the Science Students’ Society. This leading organisation is one of the three faculty pillars: the academic and support staff, and the student body. Together, we have made giant strides and the future looks bright.
Special thanks to Prof. Stanley Fiorini who helped us compile our timeline, aided by Prof. Josef Lauri.
Into The Crystal Maze
To many, crystals are pretty and mysterious rocks with magical properties. But real crystals are nothing of the sort. They are groups of atoms or molecules arranged in a highly regular way. Their study is important in many fields including chemistry, biology and pharmaceuticals. Dr Liana Vella-Zarb, Dr Rosalin Bonetta and Dr Daphne Attard explain to Francesca Vassallo why crystals are better than diamonds.
Science unchained
Lucia Farrugia, vice-president of S-Cubed, gives us her opinion on the development of the Faculty of Science.
Every Breath You Take
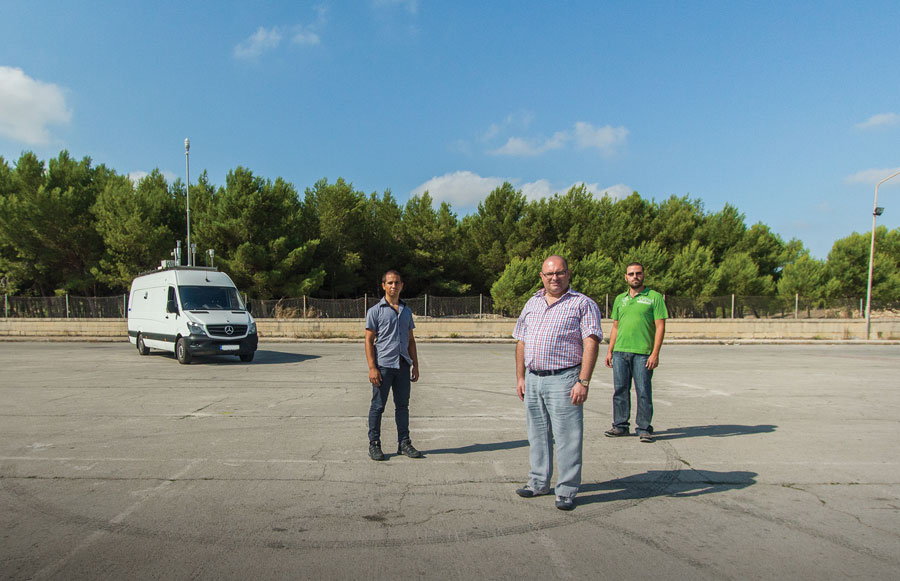
The air we breathe is vital to our health. Researchers at the Department of Geosciences (University of Malta) are measuring how clean Malta’s air is. They are also optimising a model of the Mediterranean atmosphere to see how climate change will affect the Maltese Islands and their surrounding region. Words by Natasha Padfield. Photography by Jean Claude Vancell.
The Underbelly of the Graph
How does Facebook suggest new long lost friends? And, how does Google get your searches right so often. The answer is Graph Theory, an area of mathematics being investigated by Prof. Josef Lauri. Dr Claude Bajada finds out more.
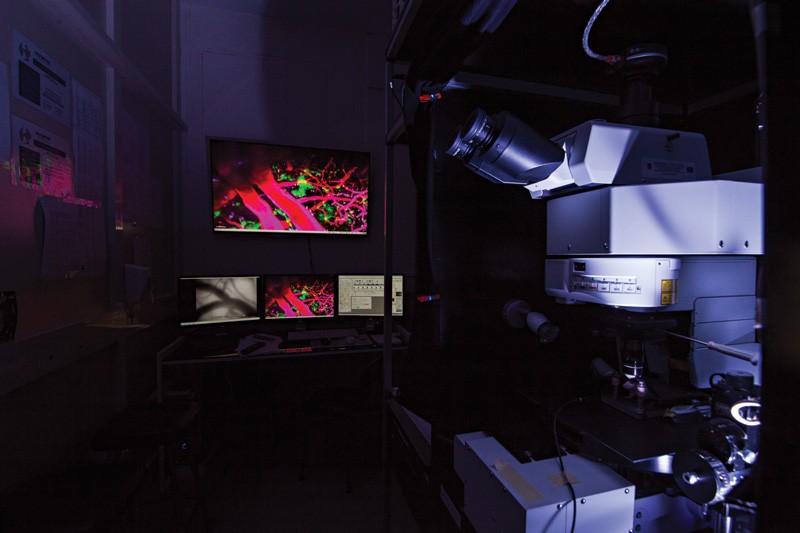
Of Mice and Microscopes
Colour Chemistry in Water
Written by Maria Cardona
Atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels have increased dramatically in the last few decades. Famous for causing global warming, CO2 is also resulting in the acidification of seas and oceans. This disturbs the rich life of the marine ecosystem, which affects human communities dependent on this environment for their livelihood. For islands like Malta and Gozo, this problem is particularly important. This ‘silent crisis’ has attracted the X-prize Competition organisers who have set a $2 million dollar prize to be awarded to anyone that can develop stable, inexpensive, and precise acidity (pH) sensors to help understand the acidification of marine environments. At the same time, a European COST initiative (Supramolecular Chemistry in Water) is encouraging the design of water-soluble molecules which can recognise analytes. Most chemical sensors do not perform well in water.Continue reading
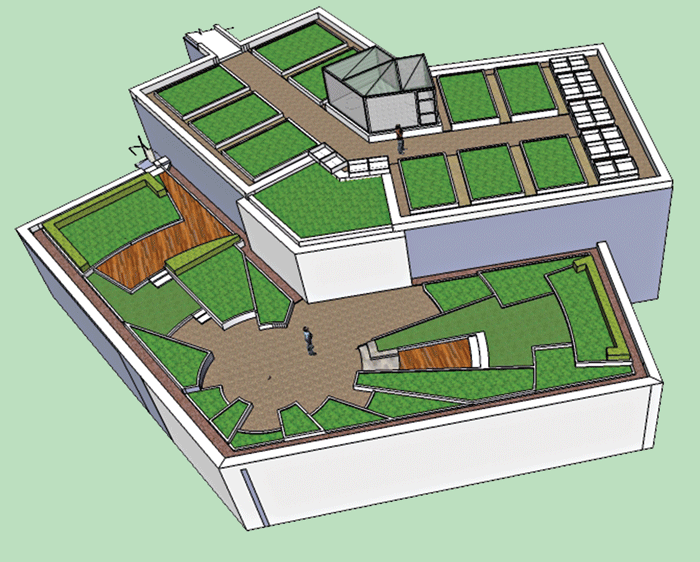
Green Roof Malta
In Malta, buildings cover one third of the Island, leaving greenery in the dirt track. Green roofs are one way to bring plants back to urban areas with loads of benefits. Antoine Gatt, who manages the LifeMedGreenRoof project at the University of Malta, tells us more.
Connect the Dots
A new hallmark for graphene, the wonder material of the 21st century, has been found. It has a range of applications—from biomedical to new, smart materials. To gain a better understanding of this discovery, Claire Testa met metamaterials researcher Professor Joseph N. Grima and his team (Department of Chemistry, University of Malta). Photos by Elisa von Brockdorff.Continue reading