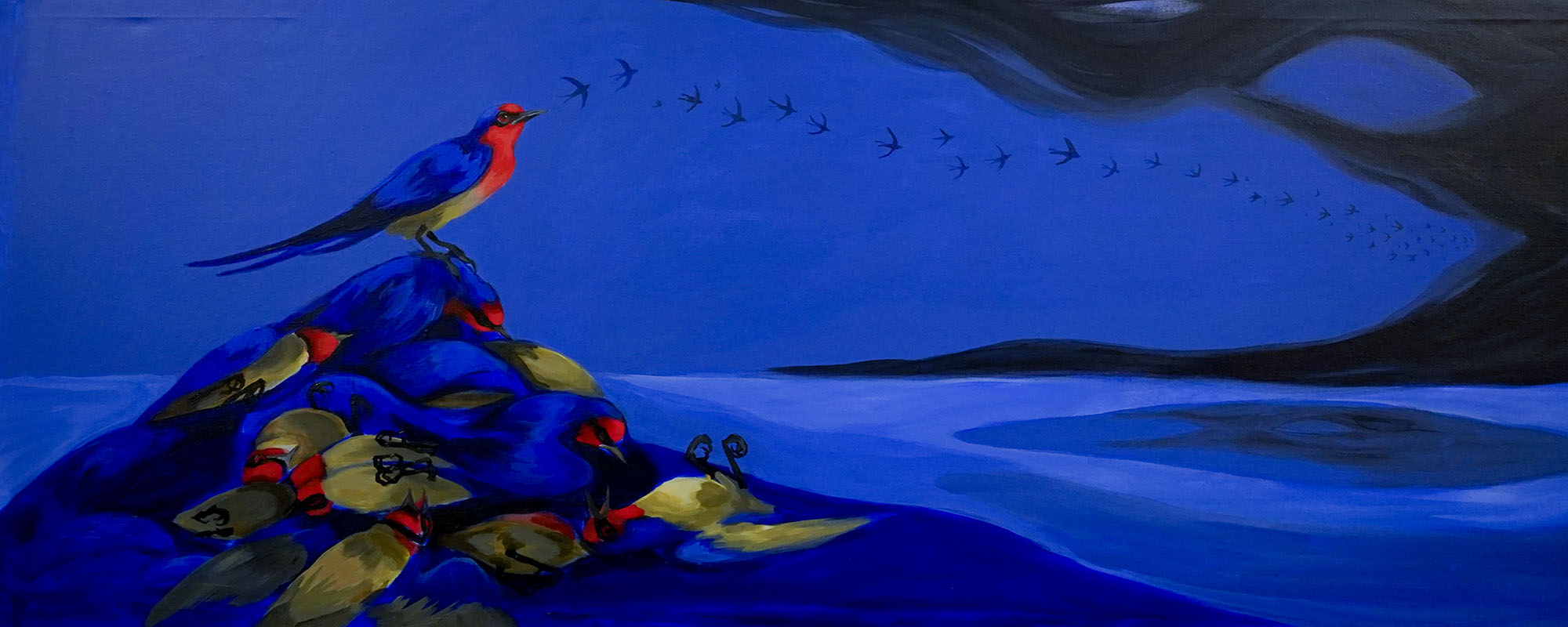
Designer and visual artist Daniela Attard, known as ielladoodle, hosted Migration Nation, a multimedia art exhibit at Spazju Kreattiv. The exhibit deals with several important issues in both a worldwide and Maltese context. THINK visits the exhibit and speaks with Iella about her work and her time as a UM student.
Continue readingCulinary Medicine: A Missing Ingredient in Medical Education
For her second-year physiology research project conducted under the supervision of Chev. Prof. Renald Blundell from UM’s Department of Physiology and Biochemistry, Courtney Ekezie focused on sustainable food systems and their impact on human health. The study briefly mentioned culinary medicine – an aspect that later inspired this article for THINK.
Continue readingPoetry in Motion: Celebrating World Poetry Day at the UM Library
Words have the power to heal, inspire, and connect. On 21 March, the University of Malta Library, in collaboration with Poetry Jam Malta, invites you to an evening of poetic expression as we celebrate World Poetry Day.
Continue readingUM’s First SEA-EU Blended Intensive Programme
In February 2025, the University of Malta hosted its first Blended Intensive Programme (BIP) on tourism sustainability in conjunction with the International Office and SEA-EU Office. THINK Editor Rebekah Zammit caught up with Dr John Ebejer from UM’s Department of Tourism Management to ask a few questions about the BIP.
Continue readingGuardians of the Lost Web
Digital archives safeguard our shared heritage, but in an era of cyber threats and fleeting information, who will protect these modern Libraries of Alexandria? THINK speaks to Dr Charlie Abela and Luke Brincat.
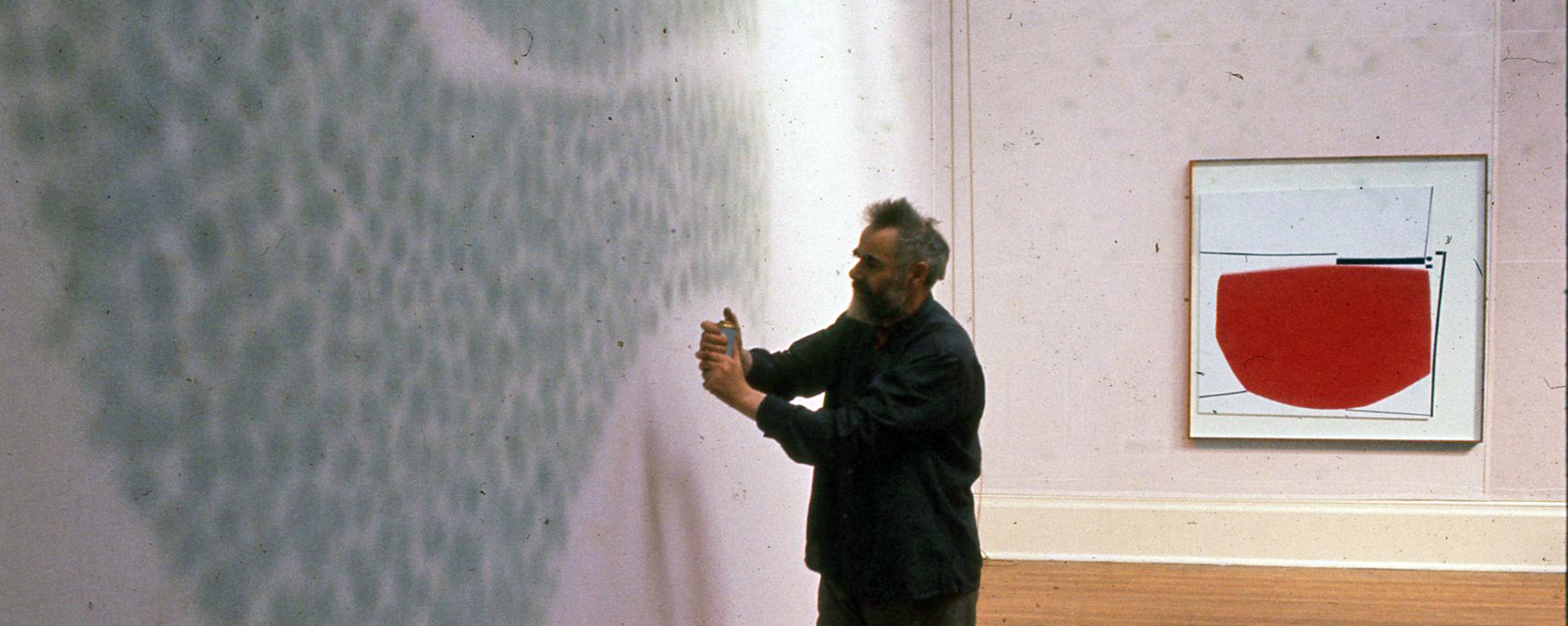
Continue readingChaotic Order: Victor Pasmore’s Abstract Art Keeps Beating
And like that, you, dear reader, and I – together, we fall into the rabbit hole of abstract art. From order to chaos. Down, down, down. ‘“I wonder how many miles I’ve fallen by this time?” she said aloud. “I must be getting somewhere near the centre of the earth.”’
Continue readingExploring Birżebbuġa through Soundscapes
Have you ever thought about the social implications of sounds? Daniel Gafà explored the locality of Birżebbuġa through its soundscapes. His study highlights the role that sounds play in shaping residents’ sense of place.
Continue readingMicromuseums with Mighty Value
University of Malta alumnus proposes the first-ever definition of a ‘micromuseum’. Dr John Vella, a doctoral graduate of the Mediterranean Institute, conducted this research after successfully defending his thesis on grassroots museums under the supervision of Prof. John Chircop. Vella continues to research and publish studies on themes concerning such museums.
Continue readingUnited in Diversity: Malta’s Annual EUNIC Festival
As Malta celebrates its 20th anniversary within the EU, the 2024 EU National Institutes for Culture (EUNIC) Film Festival showcased the power of film to reflect Europe’s cultural mosaic. THINK explores what it means to be European.
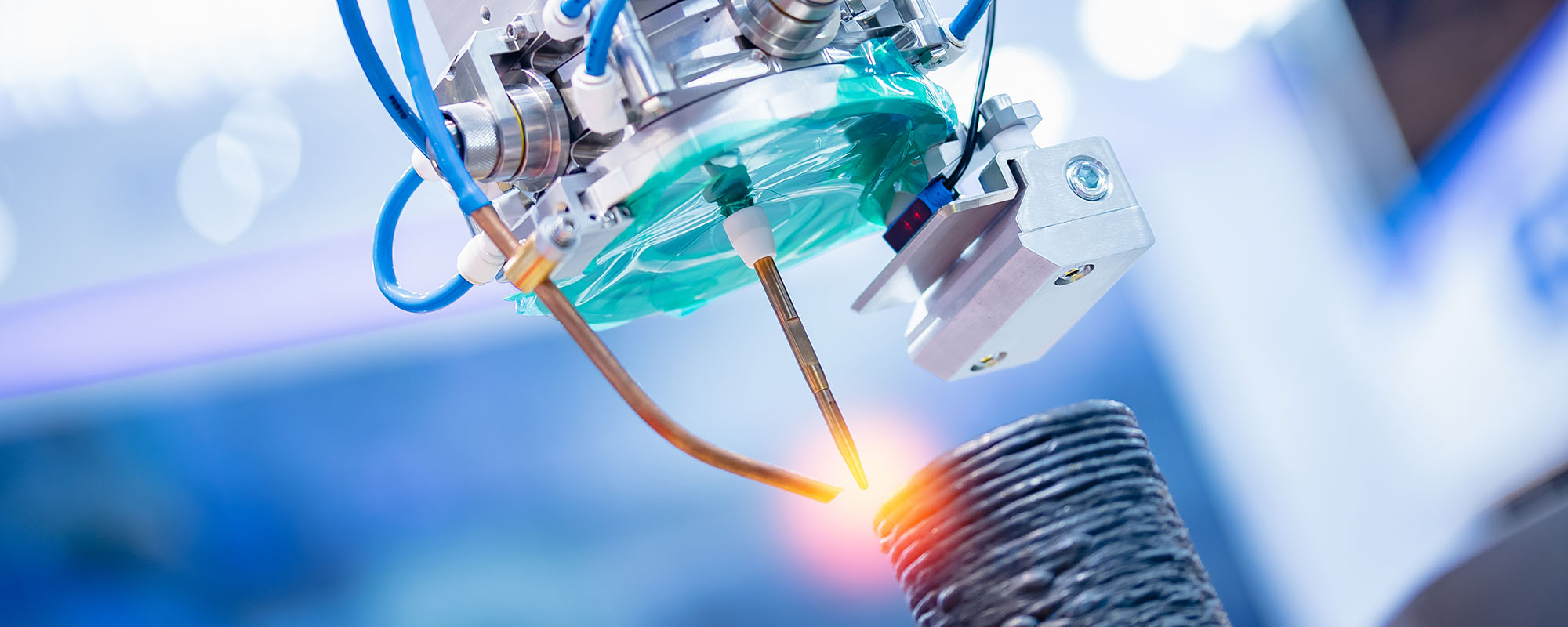
Continue readingSmooth Operator: Improving Surface Finish in Additive Manufacturing
While the advent of 3D metal printing may redefine how designers develop parts for products, the process itself is not without faults. Andre Giordimaina speaks with THINK about the GLAM Project, which aims to improve the process of 3D metal printing by optimising the finish and performance of designed parts.
Continue reading