Nearly two-thirds of the Earth is covered in water. Yet we know more about the surface of the moon and Mars than we do of our own ocean floor. Humans have an understandable fear of water and desire to remain safe on land. The oceans are formidable places requiring sophisticated equipment. Even more dangerous is exploring uncharted areas.
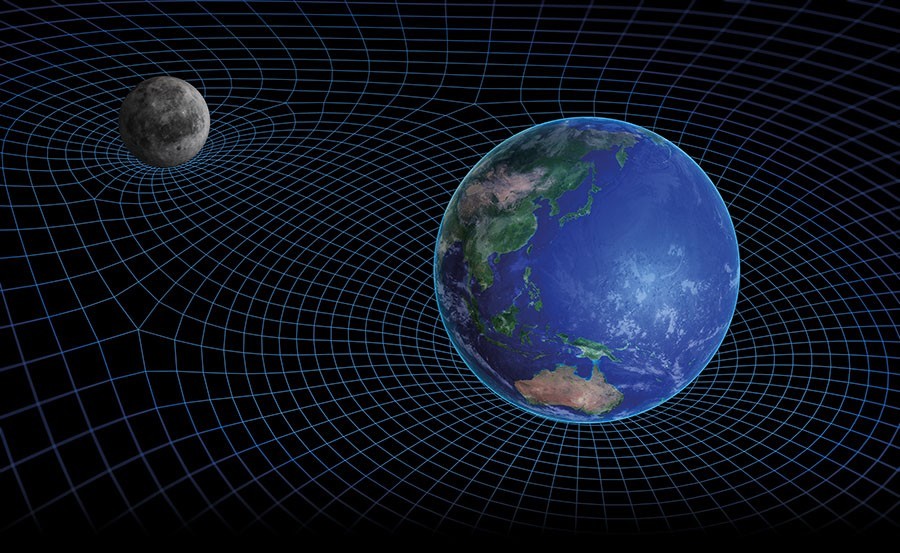
Understanding gravity to understand the universe
For a primate species clinging to a speck of dust in an incomprehensibly vast universe, curiosity has seen humans discover a great deal about how it all works. However, there are still mysteries that the cosmos is reluctant to relinquish, one of which is gravity. The most accurate theory describing gravitational attraction is general relativity, developed by Albert Einstein in 1915. Unlike Isaac Newton, Einstein did not describe gravity as a force, but rather a manifestation of the curvature of spacetime, thought of as a stretchable and squeezable fabric that is distorted by matter. However, his theory does not fully explain phenomena such as the accelerating expansion of the Universe and inconsistent orbital speeds of stars within galaxies.
Wall-E: Ta-dah!
Think sci-fi, think robots. Whether benevolent, benign, or bloodthirsty, these artificially-intelligent automatons have long captured our imagination. However, thanks to recent advances in mechanical and programming technology, it looks like they are set to break the bonds of fiction.Continue reading
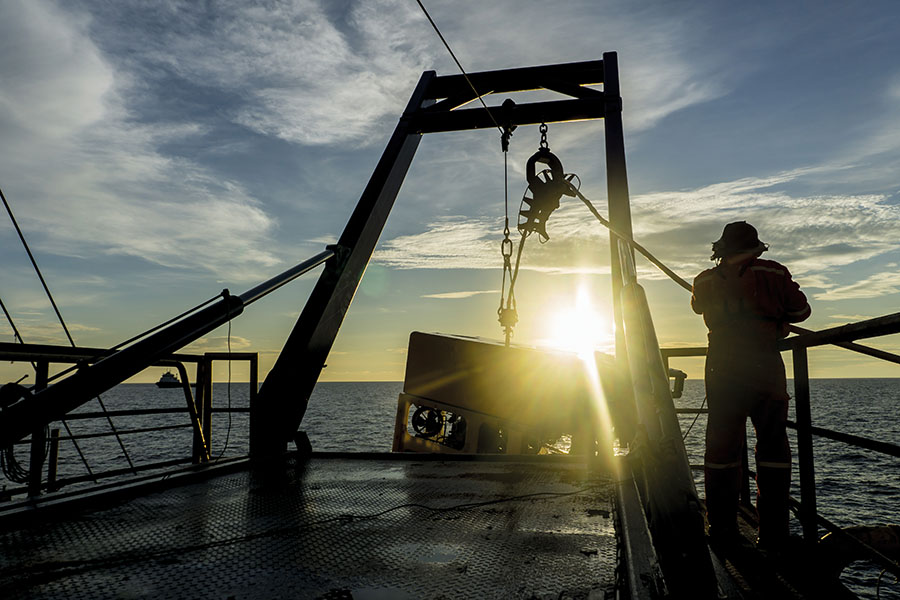
Glider South: Exploring the sea south of Malta
To map pristine areas in the Mediterranean, CAMPE is going where no glider has gone before. Prof. Aldo Drago writes.
Sounds of silence
| Tech Specs |
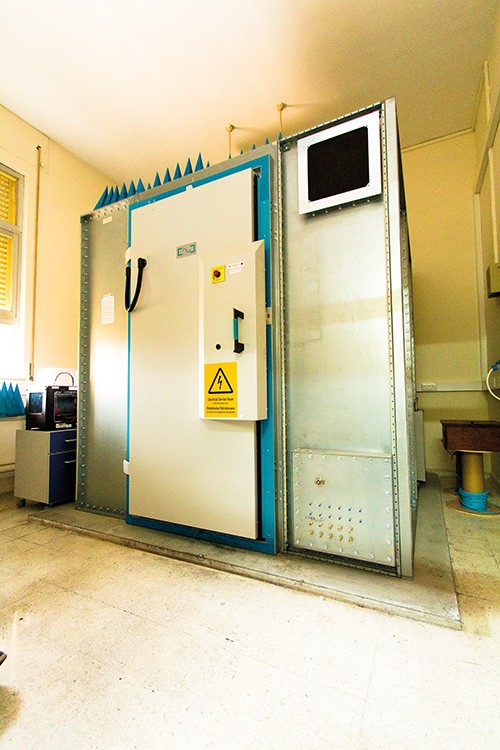

Dimensions: 2.5m x 2.5m x 2.5m Weight: 2 tonnes Frequency: 800MHz – 18GHz Price: €140,000 |
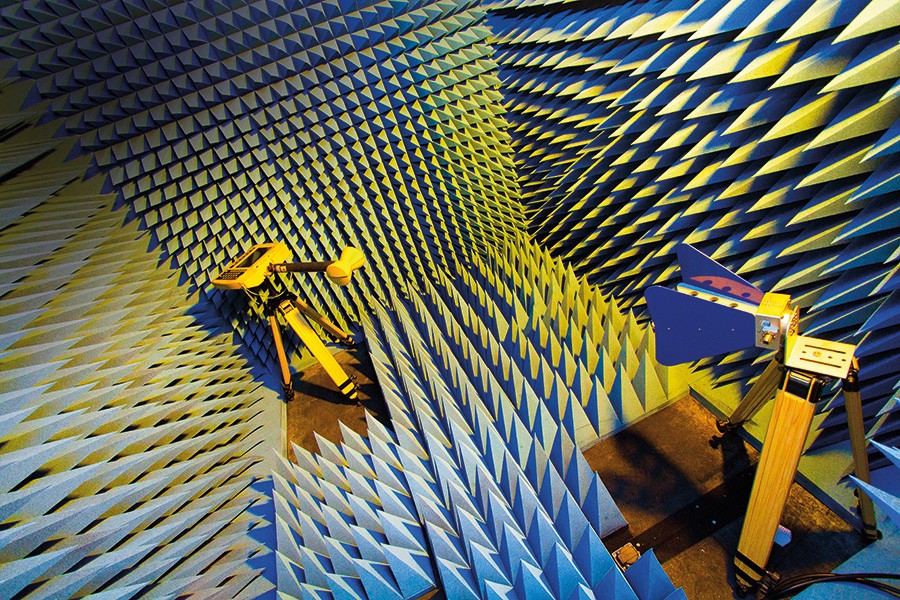
Everything in the world can emanate sound waves. These are invisible, consisting of vibrating particles in the air which can strike our eardrums, which lets humans hear. But what if you want to measure waves coming from a particular object?
An anechoic (echo-free) chamber is a heavy, metal enclosure with inner walls covered in foam wedges made from a radiation absorbent material. Any emitted sound or electromagnetic waves become trapped between these wedges until all their energy is completely absorbed. The chamber also eliminates all noise from exterior sources. Simply put, speak in an anechoic chamber, and you will hear the pure sound of your voice echo-free. The volume of these chambers is dictated by the size of the objects as well as the frequency of the device under investigation. They can be anywhere from the size of an old television monitor to the size of an aircraft hanger.
So what are they used for?
Testing electronic devices that radiate acoustic or electromagnetic waves and mapping out radiation patterns of antennas. It’s useful for systems such as satellites, radars, computers, missiles, and vehicles. Measurements aim to determine characteristics such as susceptibility, system sensitivity, effective radiated power, tracking ability, and comparability. The chambers can also be used to evaluate the effect of electromagnetic fields on human tissues, a type of experiment that has already been carried out in the University of Malta (UoM) anechoic chamber. Manufacturers of electronic equipment are required to conduct electromagnetic compatibility and immunity testing prior to placing a device on the market. This ensures that they won’t generate too much electromagnetic disturbance and will also be sufficiently immune from fields generated by other sources. Due to this new equipment, the UoM will be able to provide pre-compliance testing services to companies, which will prepare their devices for expensive compliance testing in certified laboratories, saving them a good sum of money.
Designing the factory of the future
With consumer demand reaching new highs, automation in industry is essential. Dr Ing. Emmanuel Francalanza writes about his contribution to streamlining the complex factory design process for contemporary engineers.
From smartphones, to smartwatches, smart cars to smart houses, intelligent technology is inescapable. Busier people have made efficiency a valuable currency and thus the ‘Internet of Things’ (IoT), and its plethora of connected devices, has become a necessary part of everyday life. The application of this model goes way beyond the regular consumer, however. Continue reading
Through the VR glass
As societies evolve and take in a greater number of distinct cultures, histories, and traditions, the ability to empathise with each other becomes vital, for all our sakes. In an effort to get as close as possible to seeing life through another’s eyes, researchers from the University of Malta are creating a virtual reality experience that allows users to step into someone else’s shoes.
Words by Dr Vanessa Camilleri.
From a young age we are often taught that if we want to understand someone else’s perspective, we must first walk a mile in their shoes. This ability to place ourselves in another’s position is what we call empathy. This component of emotional intelligence is known to increase prosocial behaviour and reduce individualistic traits, meaning that it can lead to a better quality of life where practiced, whether at home, in the workplace, or any other environment.
Stuck in the middle with the fumes
Since the 1960s heavy fuel oil (HFO) has reigned supreme as the king of maritime fuels. It was efficient and cheap; its use spread far and wide. International shipping boomed on its success. Even today, this industry handles 90% of the world’s trade volume. For many, HFO is the lifeblood of the maritime shipping industry. But it has a dark side…