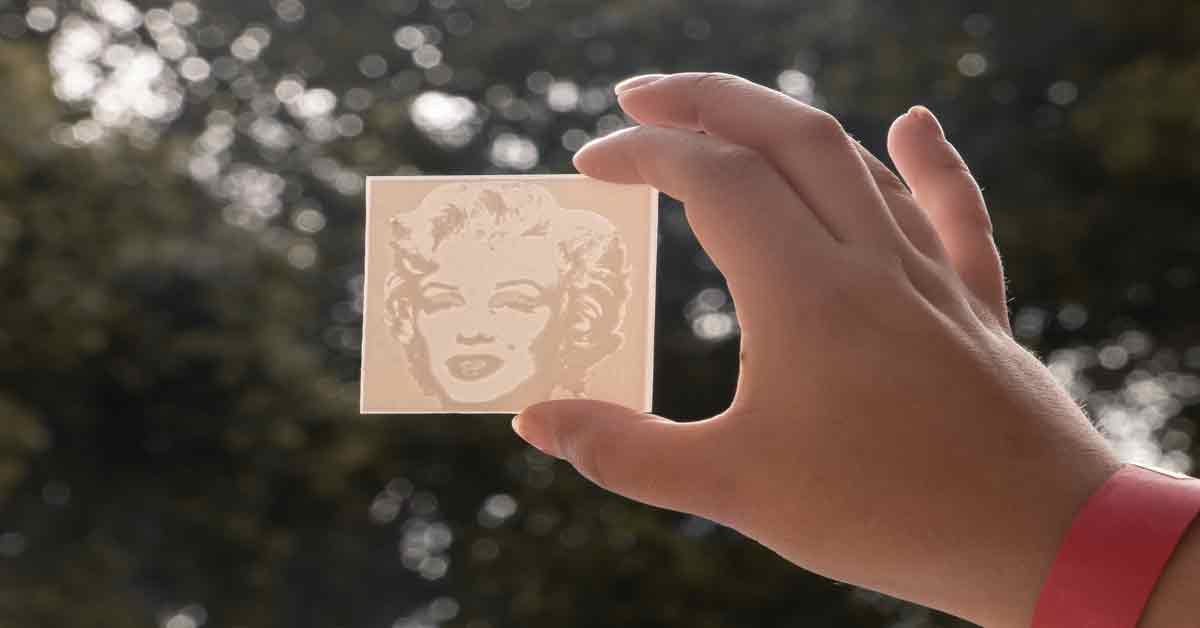
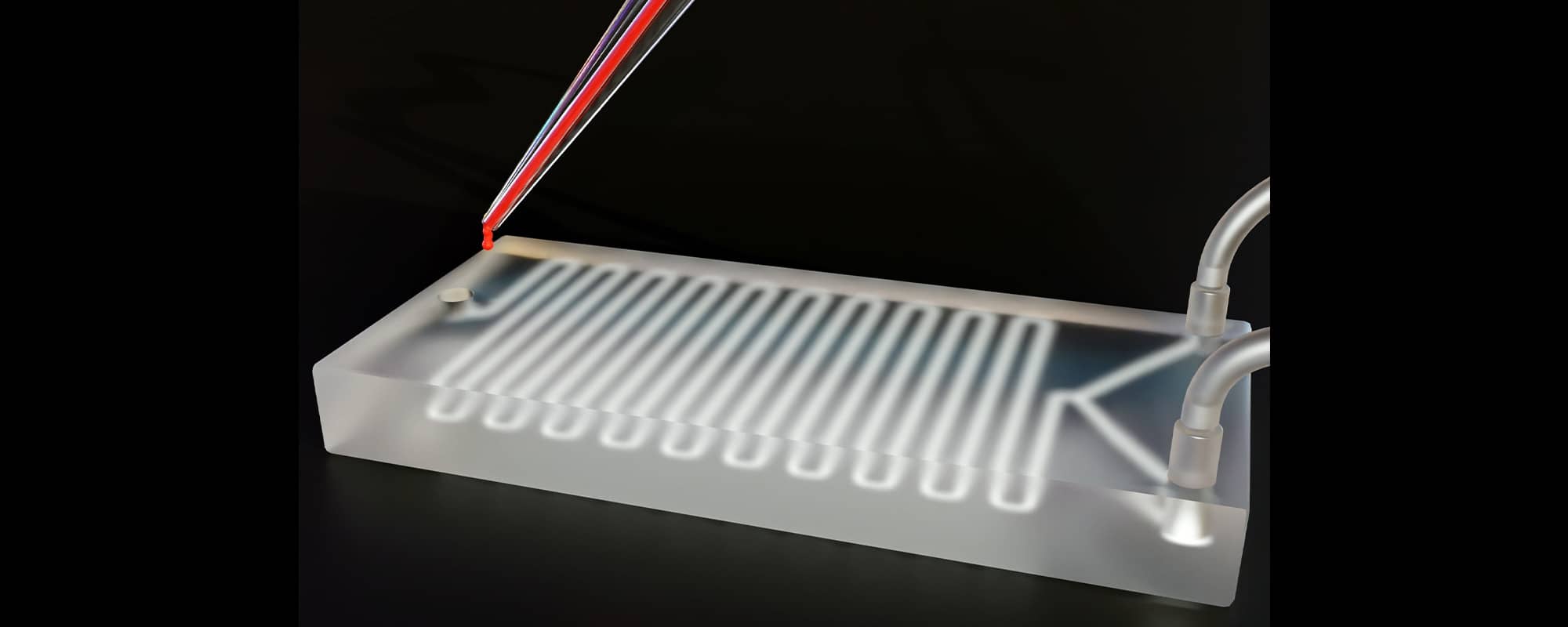
Microfluidic devices manipulate small volumes of fluids, which are mainly used in biomedical application scenarios such as clinical diagnosis, drug delivery, and point-of-care testing. Creating such devices is a costly and challenging endeavour. The UM’s Department of Industrial and Manufacturing is investigating cost-efficient ways to produce microfluidic devices faster and a lot easier.
Continue readingPreserved in Plastic
Archives help preserve the past. Modern archives are dependent on technology. What happens when the technology used to store the past becomes obsolete? Will this information be lost forever at the next update? Words by David Mizzi.
Continue readingLasers bonding layers
fused filament fabrication, laser, Laser Engineering and Development Ltd., 3D printing, Iren Bencze, Gabor Molnar, Arif Rochman
Continue readingSafe haven?

Some refer to the Venice Biennale as the pinnacle of the international art world. Last year, feathers were flurried by the Maltese delegation and their representation of Maltese identity. This year, the works question a specific part of the Maltese narrative.
‘We are working around the theme of MALETH,’ says Dr Trevor Borg, artist, curator, and University of Malta lecturer. Maleth refers to the ancient word for Malta. ‘It is also called HAVEN and SAFE PORT.’ These were all terms used in reference to Malta over the centuries. But is our island really that? This is the question being tackled by Borg and his colleagues.
Immigration has been a critical issue in recent years, creating an inflammatory divide in Malta. Borg is using the first immigrants, the animals that travelled to Malta during the ice age, to make his point. ‘They travelled here because of the heat our island provided and the food that came with it. But as the ice in the North started to melt, sea level rose and they were unable to return.’
What is the relation between an (apparent) safe haven and a heterotopia? Here, heterotopia refers to Michel Foucault‘s notion of the ‘other place’. Heterotopias are described as ‘worlds within worlds’, connecting different places. They are places that constitute multiple layers of meaning, that accumulate time, that can be both real and unreal.
To represent this visually, Borg is going to create an archaeological find with hundreds of objects from history. Animal remains will feature, as will unusual artefacts and other strange finds. Borg was inspired by Ghar Dalam and used it as a starting point, but this work is not about history. ‘My work begins at the cave. But I will then leave the cave behind and delve into a distant world that never was! The work responds to fabricated histories, museological conventions, historical interpretations, and hypothetical authenticity. It is based on pseudo-archaeological objects and imaginary narratives,’ he explains.
Collaborating on this work, bringing the artefacts to life is Dr Ing. Emmanuel Francalanza (Faculty of Engineering). The process began at the National History museum in Mdina. ‘Together we selected and scanned a number of animal bones from their archives,’ Francalanza says. This included femurs, teeth, and skulls among others. ‘I then supported Trevor in reconstructing the 3D model and preparing it for printing.’
For Francalanza, this was a chance to apply engineering technologies in new ways, to allow artists to express themselves. But not just. ‘At the same time, this opportunity provides us engineers and scientists with an avenue to explore concepts and even utilise thinking patterns which are not traditionally associated with our disciplines. It helps us be more creative and open to innovative practices.’
Working together, Borg and Francalanza are blurring the lines between what is real and what is fake. By recreating the original artefacts in such a way that a viewer cannot determine whether what is being seen is authentic, the project is poignant commentary for the post-truth era we are living in.
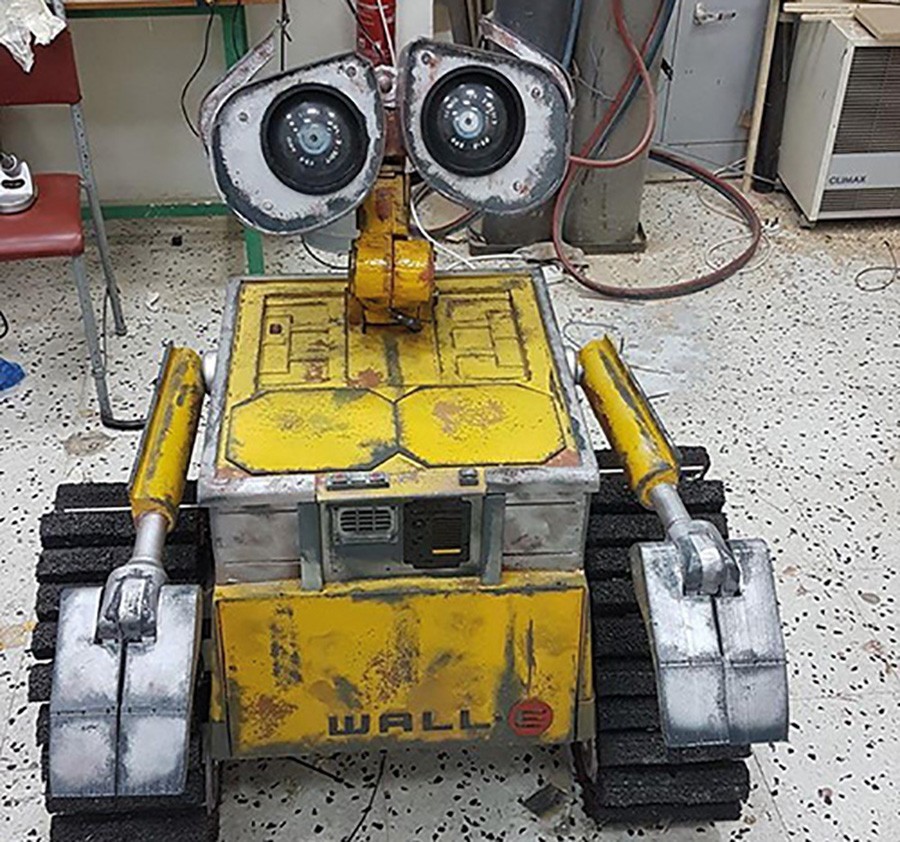
Wall-E: Ta-dah!
Think sci-fi, think robots. Whether benevolent, benign, or bloodthirsty, these artificially-intelligent automatons have long captured our imagination. However, thanks to recent advances in mechanical and programming technology, it looks like they are set to break the bonds of fiction.Continue reading
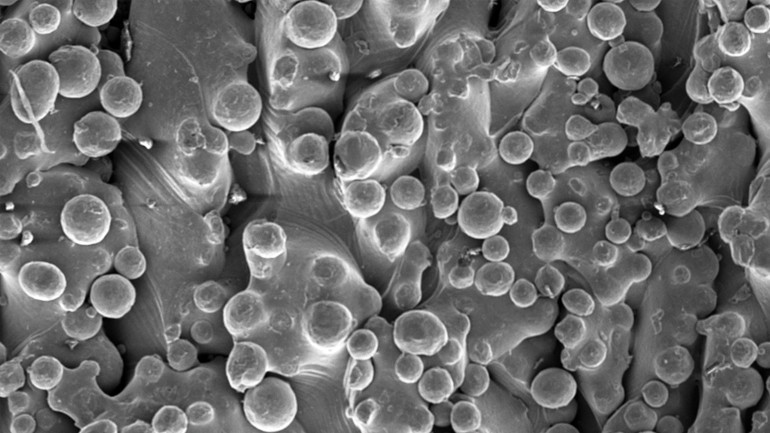
Titanium: Smoother and shapelier
Electron Beam Melting (EBM) is a state of the art manufacturing process. Using this process product designers will be limited only by their imagination. This technology uses an additive manufacturing approach where parts are built layer by layer — think of ‘3D printing’. It can use exotic metals like titanium alloys, however it does have limitations such as producing a rough surface finish that hampers its functions.
Christian Spiteri (supervised by Dr Arif Rochman) investigated whether the Electric Discharge Machining process can be used to finish parts produced using EBM to give a smooth surface (difference pictured). He treated titanium products with the Electric Discharge Machining process and microscopy showed that the finished surface consists of a set of micro-craters instead of rough grains. By adding the finishing process, more complex geometries could be created. Overall, adding Electric Discharge Machining to EBM had many benefits.
Dr Arif Rochman (University of Malta) said, ‘EBM parts can be used for a wide range of applications such as implants in the medical sector or complex tool inserts, […] which cannot be manufactured using conventional methods. Understanding the synergy between both processes is a must for product designers and process engineers to be able to manufacture high quality EBM products.’
This research was performed as part of a M.Sc. (Res) in Mechanical Engineering at the Faculty of Engineering. This research was partially funded by the Strategic Educational Pathways Scholarship (Malta). This Scholarship is part-financed by the European Union – European Social Fund (ESF) under Operational Programme II – Cohesion Policy 2007-2013, ‘Empowering People for More Jobs and a Better Quality Of Life’.