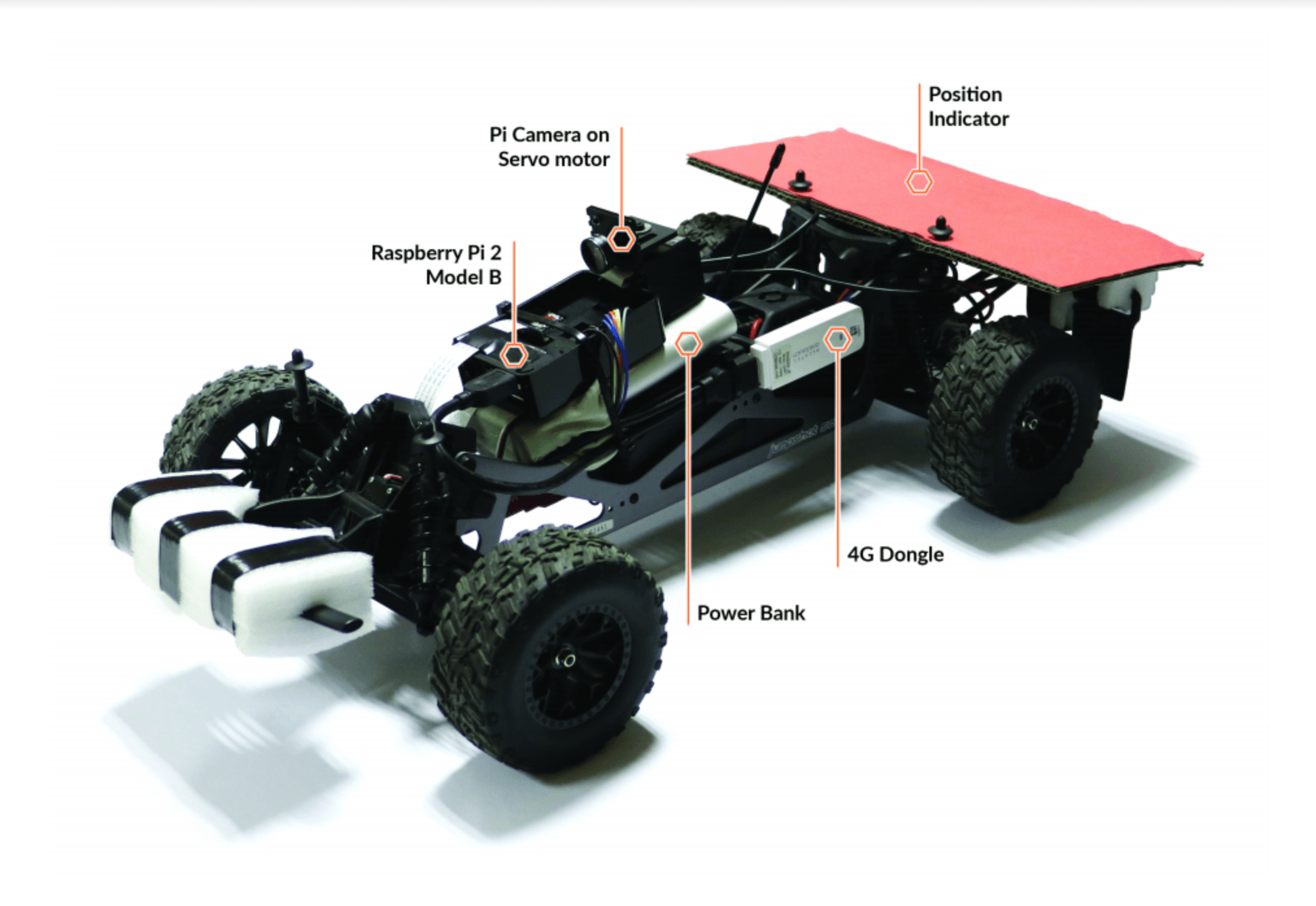
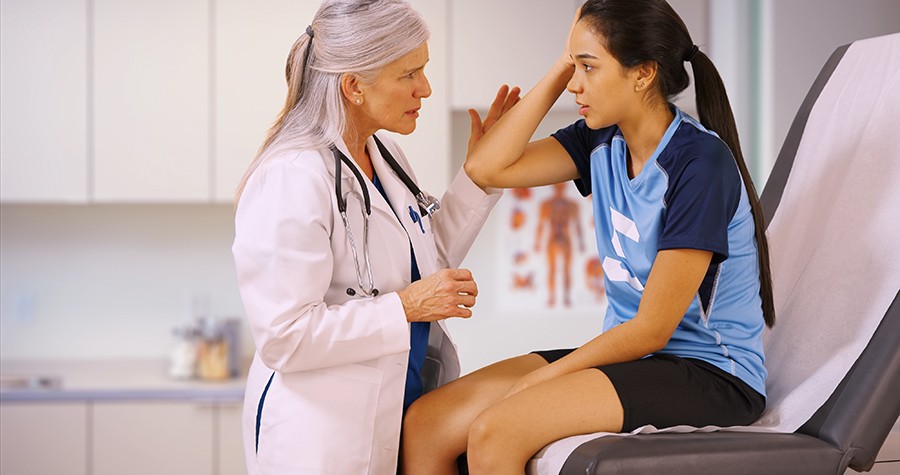
For the first time in Malta, a cardiac screening programme for young people aims to identify who among them are most at risk of sudden cardiac death. Here, Laura Bonnici chats with Dr Mark Abela to learn more about the Beat It project and the impact it is having on young lives across Malta.
There are times in life when death haunts us all. It is most tragic when it strikes down our youth. This year, Italian footballer Davide Astori and Belgian cyclist Michael Goolaerts made headlines after they died unexpectedly. Also making headlines was sudden cardiac death (SCD).
Ischaemic heart disease is the most common cause of cardiac deaths, its likelihood increasing with age. A blockage in one of the arteries supplying the heart starves it of oxygen and nutrients, leading to heart attacks, sometimes resulting in cardiac arrest, in which there is sudden and unexpected loss of electrical heart function. But SCD in young people is very different from cardiac death later in life.

Much like Astori and Goolaerts, SCD victims are generally presumed to be in good health. Early symptoms are often incorrectly attributed to other issues or life changes. The result is a horrendous loss for the sufferer and their family and friends, who also have to weather biological, psychological, and social repercussions. Seeing these events unfold, specialist trainee in Cardiology Dr Mark Abela felt the time was right to offer an SCD screening programme to young people in Malta. He called the project Beat It.
The idea behind Beat It was inspired by the UK-based NGO Cardiac Risk in the Young [CRY], Abela notes. ‘CRY offers screening to young people between 14 and 35 to identify those who might be prone to heart disease. They then give follow-up advice, support, and evaluations accordingly. I realised that a similar programme would be very beneficial to young people here in Malta,’ says Abela.
In Malta, the Beat It project has focused mainly on fifth form students between the ages of 14 and 16. The cardiac screenings attempt to identify those who may be susceptible to SCD, with those prone to it referred to hospital for further tests to catch the condition before it can strike.
‘Because athletes are believed to be at a higher risk for SCD, we need to have routine screening across all sporting disciplines,’ says Abela. ‘Sport has shown the medical community that young individuals who are susceptible to genetic heart disease are still at risk of SCD. Screening helps decrease this burden. Current evidence also supports that this risk is present for non-athletic youths—so why neglect these youngsters?’
Launched officially in October 2017, the Beat It project saw nine doctors, accompanied by a team of technicians and nurses, going into schools and running screenings. Students filled in a simple questionnaire and took an Electrocardiogram (ECG) test on the spot. ‘We analysed the results in the hope of identifying heart disease in the early stages, then advised the young people if they should consider some lifestyle changes,’ says Abela. This included advice ranging from easing up on tennis, to which career choices might be most appropriate for the student based on their health. The team also advised further medical treatment and organised follow-up appointments with specialists Dr Mark Sammut, Dr Tiziana Felice, and Dr Melanie Burg in some instances. In the end, the project screened 2,700 of the 4,300 eligible fifth form students across Maltese schools, all with the support of the school administrators and teachers, who ensured that everything ran smoothly.
The significance of this project could also reach well beyond the lives of the young people themselves. ‘Since the country is so small and families are often inter-connected, genetic diseases in Malta tend to be more prominent,’ Abela emphasised. ‘The discovery of susceptibility to hereditary cardiac disease in any young person therefore also suggests that their parents or siblings may be at risk of SCD. With appropriate testing, the ripple effect of Beat It could preempt problems in entire families, maybe even saving someone’s life in the process.’
The project boosted awareness of cardiac disease and SCD for Maltese young people, their parents, and their teachers. UK data reports that eight out of 10 young deaths do not report symptoms beforehand. There is also a tendency for symptoms to be downplayed by educators who are not aware of potential problems. With this in mind, Beat It will also act as a learning platform. Since young people with cardiac abnormalities are at higher risk for exercise-related symptoms, physical education teachers are now more aware about potential red flags.
Celebrating the completion of the Beat It project, Abela expressed his gratitude for the team who made it possible. ‘The incredible dedication and teamwork of everyone involved has helped Beat It to effect positive change in young people’s lives, potentially saving some in the process.’
Note: The Beat It project is a collaboration between the Cardiology Department at Mater Dei Hospital, the Ministry of Education, the University of Malta, and the Malta Heart Foundation and is supported by corporate sponsors including Cherubino Ltd. through the Research, Innovation and Development Trust (RIDT) and TrioMed.
Author: Laura Bonnici



 With further questioning, we also came to realise that different parents have different criteria when deciding to buy a toy. One parent told us that before buying a toy for her daughter, she would ‘try to see for how long she will play with it and what the toy will give her in return.’ Another parent, concerned about toys’ safety, checks for the
With further questioning, we also came to realise that different parents have different criteria when deciding to buy a toy. One parent told us that before buying a toy for her daughter, she would ‘try to see for how long she will play with it and what the toy will give her in return.’ Another parent, concerned about toys’ safety, checks for the