In 2016 a 40-year-old technology company owner called Joshua Brown was killed when his autopiloting Tesla Model S malfunctioned. Since then a number of other incidents have raised the problem of safety in and around autonomous cars. One potential solution is to connect cars together so that they can keep in constant touch, letting each other know exactly where they are and when to get out of the way. Another alternative is to have a human pilot the vehicle for part, or all, of the journey, reducing some of the fear associated with self-driving cars’ safety and giving rise to so-called remotely-piloted ground vehicles (RPGVs).
Because this idea needs a stable and constant Internet connection, I wanted to test if the current 4G network is fast enough for these cars to drive and function safely. Relying on a hefty amount of external data about pedestrians, other traffic, road layouts, and more makes things difficult.
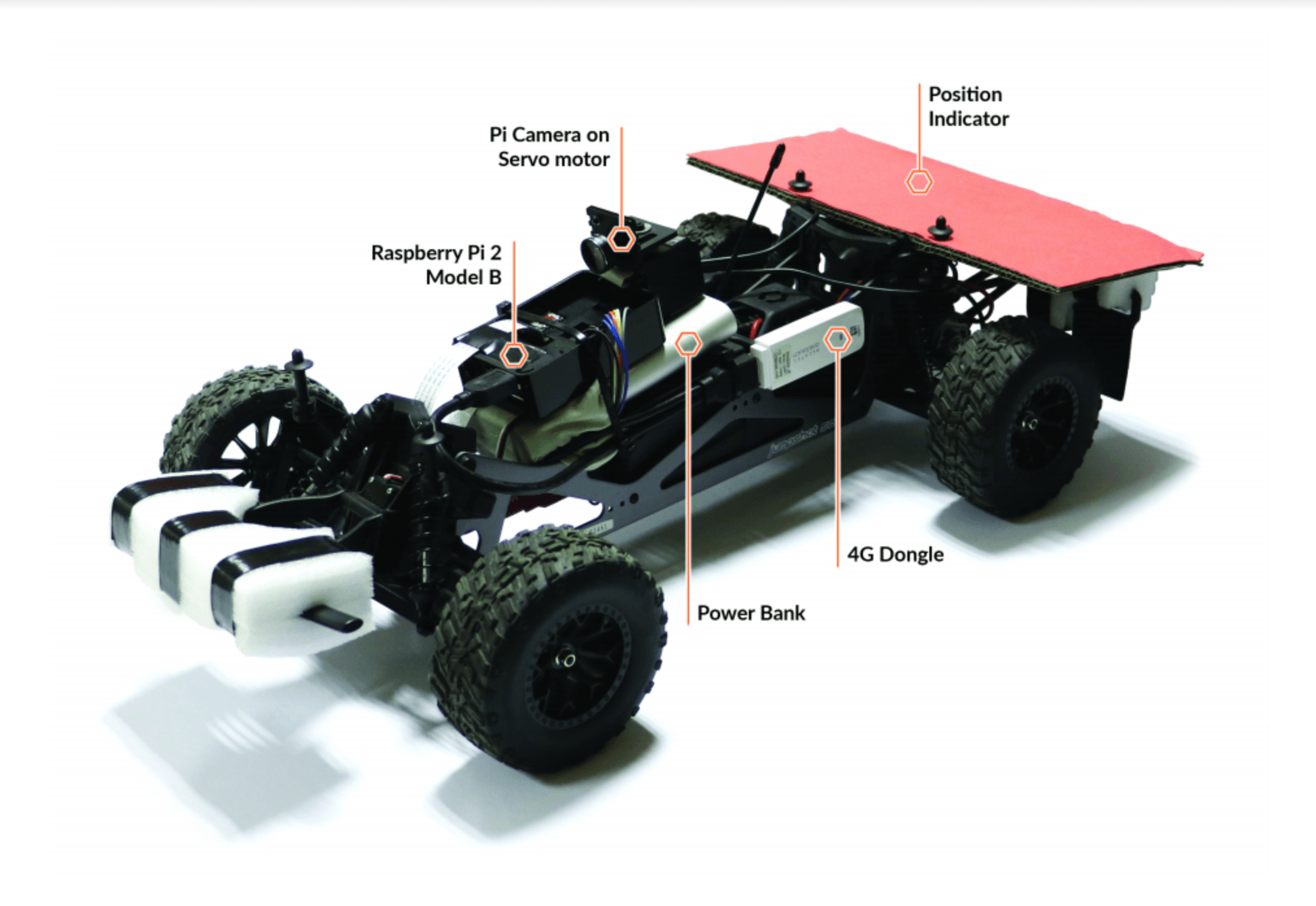
At the Department of Communications and Computer Engineering, (Faculty of ICT, University of Malta [UM]), on a project led by Prof. Ing. Saviour Żammit, we created an RPGV by modifying a radio-controlled vehicle and used it to test the suitability and safety of 3G, 4G, and Wi-Fi networks.
Fast communication between driver and car is crucial for the safety of RPGVs. If information from the car takes too long to reach the driver, they won’t be able to react quickly enough to avoid obstacles and accidents.
On Wi-Fi networks, we found that when the connection moved from one base-station (the receiver-transmitter that serves as the hub of a local wireless network) to another, the handover took too long. This problem meant that whilst the connection was transferring, the video was lost, leaving the car blind. This is obviously dangerous and means that these networks are not safe enough for automated cars. 3G was not fast enough to transmit video in real-time.
The next step was to set up an outdoor racetrack to test the RPGV over the 4G network on UM grounds. We varied the networks’ signal delay and the camera’s range of view, then measured the lap times, distance travelled and road cones hit to calculate driving accuracy. Finally, we compared them to how accurate the drivers thought they were driving.
We concluded that 4G mobile networks allow adequate remote control of an RPGV, although the amount of delay left little room for error. A faster 5G network would be able to act quickly enough to avoid accidents, so self-driving cars will need to wait a bit longer before becoming a reality.
This research was carried out as part of the Masters of Science (Telecommunications) program, Faculty of ICT, UM, supported by GO plc and the Research Fund Committee of the UM.