Let us fish4tomorrow
All over the world, governments and stakeholders are trying to cope with overfishing. Overfishing is when too much fish is caught which leads to an overall degradation of the marine ecosystem. It is the non-sustainable use of ocean resources. Words by J.D. Farrugia
Continue reading
Placing Cultural Research on the Map
The Valletta 2018 Foundation recently started a five-year research study to evaluate and monitor the European Capital of Culture (ECoC) project in Malta. The process combines both quantitative and qualitative approaches to collect data that will be communicated to the general public and interested stakeholders. This research will provide feedback to help fine-tune or correct the Foundation’s operations. The process aims to provide a local model for research in culture and the creative sector in order to encourage more cultural research after 2018.Continue reading
Getting the Rhythm
Music has changed society. Stephanie Mifsud met ethnomusicologist Dr Philip Ciantar to talk about music from all over the world. Studying diverse musical traditions has taught him about himself and how music can bridge cultural divides to bring us together
Classical, romantic, baroque, rock, hip hop… music continues to change throughout the years, yet we all look for that beat that gets us moving. How can we not when music is such an important part of our life?
Music is found everywhere: on television adverts, films, on the radio and at places of worship. Our society immerses us in it for hours every day. A person will listen to music that represents the way they feel. Music has the potential to influence moods, feelings, and thoughts.
“Music opens infinite thinking modes unknown to us and uncovers situations we wouldn’t otherwise experience”
Legendary rock guitarist Jimi Hendrix, told Life magazine in 1969, ‘I can explain everything better through music. You hypnotise people to where they go right back to their natural state, and when you get people at their weakest point, you can preach into their subconscious what we want to say.’
Music, like language, has a common factor: a person’s active role. People create music. No music can exist without the people who make it.
The Ethnomusicologist Dr Philip Ciantar (University of Malta) is interested in both the music itself, as a humanly organised sound, and the musicians. His research focuses on understanding how people worldwide think about music and how that affects their music. He meets and interviews countless musicians and their audiences. People’s thinking about music is shaped by who they are, their world-view, and how they use their creative imagination to create music. Take John Lennon’s song Imagine. The song has touched countless around the world. It might have changed the way people see themselves, relate to the people around them, and influenced future songs.

Music to say ‘Hello!’
Ciantar explains that ‘by listening to and exploring music from different countries we can understand other cultural and social realities. Music opens infinite thinking modes unknown to us and uncovers situations we wouldn’t otherwise experience.’ According to him, ‘music can highlight social issues or it can make a connection with different cultures when many other avenues fail’. This is the acceptance of ‘otherness’, the concept of what makes us different from each other culturally and socially. Music can be a very effective medium.
Acceptance of different cultures needs to be taught from a young age. Music can help in showing people the advantages of multiculturalism. Ciantar suggests that, at school, children can be taught instruments used in different cultures. This would help students understand and appreciate not just the instruments but also the musicians playing them. He continues, ‘you need to be open to other opinions, cultures, and traditions’ and music provides the right scenario.
Understanding music globally should lead to appreciation of diverse sounds and how they are made, communicated, and transformed into meaning. The musical process reveals humanity and here otherness surfaces as a challenge for us to deal with. It is up to us to then connect with different cultures we might consider alien.
People come together through music. The village feast is Malta’s best example of unity through music. During a feast a quiet pjazza transforms into a music concert, a fireworks festival, and a food extravaganza — uniting the whole community. These celebrations bring people together ignoring their differences.
Multiculturalism is a worldwide phenomenon. Malta is becoming multicultural and, as Ciantar comments, ‘music is an indicator of what is going on. Performances of African music at the Marsa Open Centre can be interpreted as a plea for social acceptance and cultural integration. Slavic street players in Republic Street play Bach’s violin partitas to make us connect with them culturally. Once we are connected they play a nostalgic lullaby from their homeland to make us feel the pain of distance and sympathise with them. Undoubtedly, music serves as a social text; in itself, an intriguing sonic document that links the evident with the untold or even ignored.’ This is the power of music and the concept of otherness that can shape our thoughts on multiculturalism and readiness to accept others’ views.
“Undoubtedly, music serves as a social text; in itself, an intriguing sonic document that links the evident with the untold or even ignored”

He became even more aware of multiculturalism while conducting his Ph.D. research. He went to Libya to experience different cultural backgrounds and traditions. He worked with Libyan musicians, attending their rehearsals, talked to people on Tripoli’s streets about the musical tradition of ma’lūf (a tradition valued for its Andalusian legacy), and sneaked in percussion performances with Libyan musicians. Apart from writing a book, these experiences helped Ciantar understand otherness and the challenges it implies.
Ciantar’s first experience with ethnomusicology and otherness goes back to 1991, when he was inspired by the writings of John Blacking and Bruno Nettl, and started researching Maltese folk music għana. He saw how the għanejja performed in two different contexts and their music changed accordingly. The music they sang was more elaborate in their regular bars when compared to stage music with an unknown audience.
Otherness can also be scrutinised through musical translation. Ciantar researches musical translation: how we digest and eventually accept music that might not be initially appealing to us. Recently, he composed a Maltese festa band march out of tunes that he had recorded in Libya. The process allowed him to investigate the music and himself. He had to take elements of one musical tradition and apply it to another that was culturally remote, using himself to understand the process of how a person thinks and transforms thought into music.
Ciantar is very hopeful of the musical evolution in Malta as this is being influenced by the different cultures that people encounter everyday. This will create a more varied musical scene. Ciantar can already feel the difference.
Stephanie Mifsud is part of the Department of English Master of Arts programme.
[ct_divider]
Find out more:
-
‘The Process of Musical Translation: Composing a Maltese Festa Band March from Libyan Ma’lūf Music’, Ethnomusicology, 57(1): 1-33 (2013).
-
The Ma’lūf in Contemporary Libya: An Arab Andalusian Musical Tradition. Burlington, VT: Ashgate. (2012).
-
‘From the Bar to the Stage: Socio-cultural Processes in the Maltese Spirtu Pront.’ Music and Anthropology in the Mediterranean Online (2000)
John Lennon’s Imagine
Andalusian Music
Għana Maltija—Traditional Maltese music
Saving Malta’s Music Memory
Maltese Music is being lost. Along with it Malta loses its culture, way of life, and memories. Dr Toni Sant is trying to change this trend through the Malta Music Memory Project (M3P)Continue reading
Experiencing Stories
Earlier this year, the Valletta 2018 Foundation invited three tutors from the University of California to Malta to teach an intensive two-week course on screen-writing called Story Works to aspiring writers and producers. Two of the participants of the course, Kenneth Scicluna and Marta Vella fill us in on their experiences.Continue reading
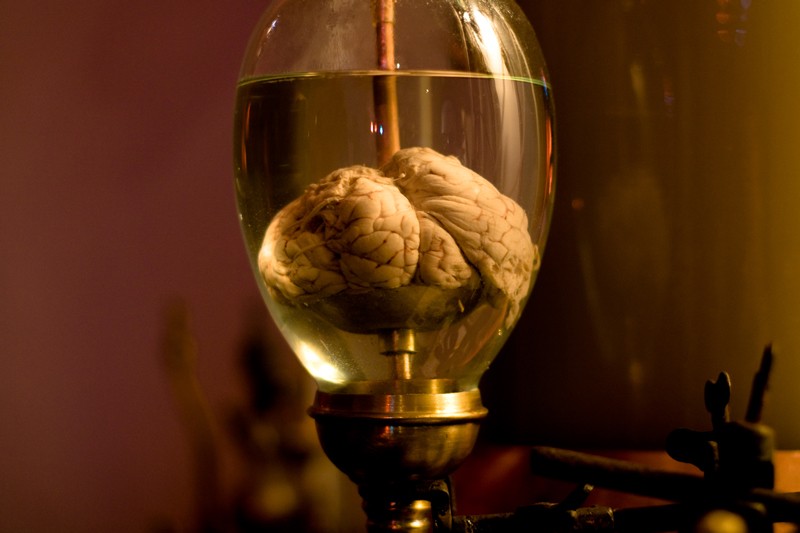
Does Alcohol kill brain cells?
This myth is HUGE! Urban legend says that drinking kills cells, some even say: ‘three beers kill 10,000 brain cells.’ Thankfully, they are wrong.
In microbiology labs, a 70% alcohol 30% water mix is used to clean surfaces pretty efficiently. It seems our neurons are made of sturdier stuff.
Alcohol does affect brain cells. Everyone knows that and it isn’t pretty. Alcohol can damage dendrites, which are delicate neural extensions that usually convey signals to other neurons. Damaging them prevents information travelling from one neuron to another — a problem. Luckily, the damage isn’t permanent.
Through the Looking Glass
What’s your favourite game? Pacman? Doom? World of Warcraft? Most of us have spent hours immersed in video games, many still do. Prof. Gordon Calleja studies why and how we get so involved in games. Science writer Dr Sedeer El-Showk found out about Calleja’s latest book and game that are gaining worldwide fame.
Hotline Miami
Push start. Grab a weapon. Get shot. Repeat… ad infinitum. ‘Punishing’ hardly describes a session of Hotline Miami. Typically, within 10 seconds you could die three or four times. It is just as frustrating as it is challenging. Addictively, you will not give up until you pass that sneaky little passage.
Hotline Miami is an ultra-violent, psychotic game, where your only aim is to kill all the ‘bad guys’.
Yet, every little move counts, and deciding which weapons to use or which door to open first will reveal the deep strategic possibilities of the game’s intense experience. As you make your way through a pile of corpses, the suspense builds up to unbearable levels as you risk losing all in-game progress for just a little mistake. The massacre is only interrupted by brief moments that reveal details of our mysterious ‘hero’s’ back-story. Keeping true to expectation, even these interludes are awkward if not disturbing, and hardly shed light on our displaced, faceless avatar.
The excellent game tops it all with an irresistible ‘80s aesthetics and a neurotic electronic soundtrack. You’ll quickly find out why this game has stolen the show winning so many awards, and has hooked fans of Grand Theft Auto and of good old shoot’em up games. Hotline Miami is a joy in repetition, providing that being stuck in a Clockwork Orange–like scenario is your idea of joy.