Over the last few decades researchers have been unravelling the truth behind marijuana. Prof. Giuseppe Di Giovanni tells us more about its use in medical research.
Continue readingBeyond Lab Coats and Microscopes
 Pride. That’s what Enrico felt when his name was announced at the Science Expo as the winner of the NSTF Contest for young scientists. The contest is a first step helping to build what Enrico Zammit Lonardelli calls his ‘scientific character’. It is a journey that led him to compete on an international level in Milan to represent Malta, meet and talk to incredible people, and learn about the way in which science is carried out all over the world. Feelings of honour, fulfilment, and success quickly followed. ‘Being surrounded by the best people in Europe in all possible aspects and fields of science was simply amazing.’
Pride. That’s what Enrico felt when his name was announced at the Science Expo as the winner of the NSTF Contest for young scientists. The contest is a first step helping to build what Enrico Zammit Lonardelli calls his ‘scientific character’. It is a journey that led him to compete on an international level in Milan to represent Malta, meet and talk to incredible people, and learn about the way in which science is carried out all over the world. Feelings of honour, fulfilment, and success quickly followed. ‘Being surrounded by the best people in Europe in all possible aspects and fields of science was simply amazing.’
Taking on such challenges in the scientific world at only 17, Zammit is the younger mirror image of another 17 year old that, around 20 years earlier, started the same journey. Today lecturer Conrad Attard (Faculty of ICT, University of Malta; Vice Chair, IEEE Malta Section) is handling several activities, one of which is an exhibit with his team for the same Science Expo which started Enrico off on his scientific voyage.
 Attard sees the Expo as a great way to distribute resources, and meet kids and visitors. ‘I want students to get excited about science and for more students to engage with these subjects’. That’s why Attard always teaches them in a fun way, by creating games were students need to solve logic problems that involve science and computing to learn and achieve their goals, and that is exactly what his exhibit at the NSTF Expo does.
Attard sees the Expo as a great way to distribute resources, and meet kids and visitors. ‘I want students to get excited about science and for more students to engage with these subjects’. That’s why Attard always teaches them in a fun way, by creating games were students need to solve logic problems that involve science and computing to learn and achieve their goals, and that is exactly what his exhibit at the NSTF Expo does.
So why is the growth of science communication important in Malta? For Attard, it is all about helping people find out what they do well in and pushing students to reach out beyond their comfort zone and that mistakes are part of the learning experience.
Zammit understands this principle. Some of his family members suffer from asthma motivating him to research it for the NSTF Expo. ‘Slowly I managed to understand the mechanism and a few questions popped into my mind. The following process was turning those questions into a project by research, planning, and finally experimentation.’
By favouring the multidisciplinary approach students are not limited to only becoming developers, but can also tackle related problems requiring knowledge or skills from other disciplines. This is what attracted Attard to the NSTF Science Expo as it uses crafts, different skills, and logic to solve problems.
 According to Zammit, the NSTF Expo and Programmes focus on analytical skills, public speaking, problem solving techniques, planning, critical thinking, creativity, and descriptive writing. ‘They all focus on character development rather than just the activity and provide an ensemble of quality development which is simply impossible to match by reading books and studying’. And, of course, there are amazing prizes.
According to Zammit, the NSTF Expo and Programmes focus on analytical skills, public speaking, problem solving techniques, planning, critical thinking, creativity, and descriptive writing. ‘They all focus on character development rather than just the activity and provide an ensemble of quality development which is simply impossible to match by reading books and studying’. And, of course, there are amazing prizes.
The Expo gave Zammit a platform for his work to be recognised by experts. ‘It has since motivated me to work harder because now I know what it feels like to win and create something useful. I want to repeat this success, hopefully at larger scales with ever bigger projects and aims.’
Maybe one day, it will be Zammit who will find himself teaching young students about science at the NSTF Expo.
The next NSTF Science Expo will be from 9–16 March for school visits, while the open weekend for everybody else will be on the 12–13 March.
For more information visit the NSTF Malta website or Facebook page.
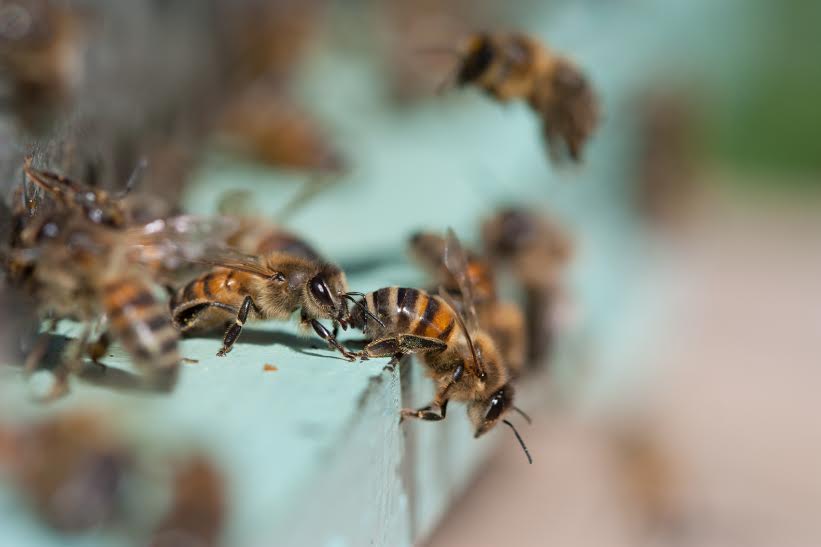
The Bees and the Bats
 What do bats, bees, wasps and flies all have in common? They are providing humans with pasta sauce for free. These organisms all pollinate our fruit on a daily basis needed to fill the grocer with all the things we love.
What do bats, bees, wasps and flies all have in common? They are providing humans with pasta sauce for free. These organisms all pollinate our fruit on a daily basis needed to fill the grocer with all the things we love.
For plants to reproduce, the most important step of the process is pollination. During pollination, pollen grains (the male cells needed for sexual reproduction) fertilise the female egg cell. This leads to seeds around which form the fruit and vegetables humans love to eat. The male and female cells are found on different parts of the flower, this is where pollinators like bees and bats come into play. They transfer pollen from one plant to another fertilising them.
Bees and other pollinators are needed for food security and economic resilience. These creatures help pollinate 87% of plant species that we use for food, material, feeding livestock, and medicine. They are essential for human diets since 70% of the world’s crops need pollinators. In Malta, crops such as tomatoes and green pepper would not grow. Bees and pollinators affect the economy, with a worldwide estimate of €153 billion. Pollinators encourage biodiversity; they pollinate crops and wild plants helping to keep the environment healthy.
The decline of bees has serious consequences for the world. So important that it was a main issue discussed by the Commonwealth countries during CHOGM (Malta, 2015) at an event organised by Friends of the Earth. Paul de Zylva (Friends of the Earth, UK) outlined the main causes as habitat loss due to urbanisation, pesticides, and climate change.
 So how do we save the bees ?
So how do we save the bees ?
Politicians, researchers, and citizens must work together to reverse bee decline. Some actions are already being undertaken. Clive Harridge (secretary general of the Commonwealth association of planners) indicated that the UN member states must include 17 sustainable development goals (SDGs) in their political policies, three of these address ecosystem threats. One of these (SDG 2) emphasises the need to end hunger by achieving food security and improved nutrition through sustainable agriculture. Another, (SDG 11) states the need to make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable. While a third (SDG 15) indicates needing to protect, restore, and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification and halt and reverse land degradation and biodiversity loss. Bees play a part in all of these goals.
Across the Commonwealth, national case studies are trying to understand the situation with pollinators to figure out how to save them. Ideas include areas where agriculture and wildlife are merged, creating habitats such as green roofs (green roofs are being built both at MCAST and the University of Malta), while some companies are even building bee hotels. Bee hotels are places where solitary bees can make nests and lay eggs without producing honey. These bees tend to be much less aggressive and thrive as long as there is enough wildlife for them to obtain food.
 Citizen engagement is needed to encourage participation to collect data and evidence. By working with researchers and policymakers real change can be achieved to save bees. Considering Malta’s situation, lecturer Dr Mario Balzan (MCAST) said at the CHOGM event that studies he was involved in showed that wild flowers growing near tomatoes helped increase their yield. Insects living on these flowers helped pollinate the tomatoes and may have acted as natural pest controls. By planting flowers in gardens and balconies bee habitat would be expanded.
Citizen engagement is needed to encourage participation to collect data and evidence. By working with researchers and policymakers real change can be achieved to save bees. Considering Malta’s situation, lecturer Dr Mario Balzan (MCAST) said at the CHOGM event that studies he was involved in showed that wild flowers growing near tomatoes helped increase their yield. Insects living on these flowers helped pollinate the tomatoes and may have acted as natural pest controls. By planting flowers in gardens and balconies bee habitat would be expanded.
There are many reasons for bee decline from uncontrolled pesticide use to widespread infections. Only by researching the problem then creatively addressing these issues can bee decline be reversed. This will require all sectors of society from citizens to researchers and policy makers to work together to save the birds and the bats.
This article featured in the Sunday Times of Malta.
Maltese Medical Minds…ASSEMBLE!
Diseases and disorders plague humanity. They have the power to devastate the afflicted and those close to them. Globally researcher are fighting back. Recently, the Maltese branch of this international force came together at the 9th Malta Medical School Conference to present their most recent findings on matters from pediatrics and public health, to the minute mechanics of the molecular world that make us all tick. Outlined here are just two examples out of over a hundred presented on the day. Words by Scott Wilcockson.
The Malta BioBank / BBMRI.mt
In the early 1990s, the Malta BioBank was started with the collection and storing of samples from all Maltese children who had been screened for rare blood disorders. Set up as a collaboration between the University of Malta and the Malta Department of Health, it was first launched using Italia-Malta project funds followed by EU pre-accession funds.Continue reading
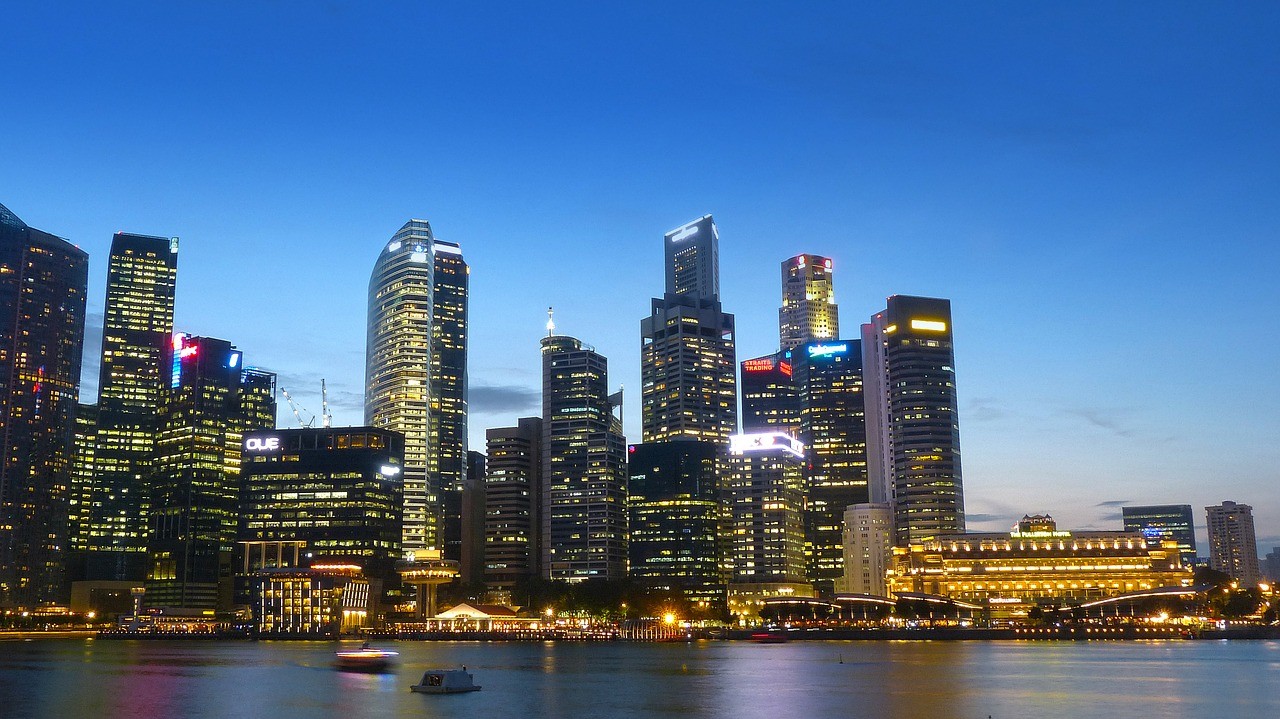
What can Malta learn from Singapore?
By Dr Andre Xuereb and Dr Edward Duca
Singapore is Asia’s success story. It has a landmass just over twice that of Malta but produces over 30 times its economic output. Singapore has invested heavily in quantum technologies, turning itself into one of the world’s leading industrial economies. Though poor in natural resources, Singapore’s investment in knowledge has resulted in it becoming one of the world’s healthiest industrial economies.Continue reading
Fly power for neurodegeneration
By Rebecca Borg
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is a neurodegenerative disease that causes motor neurons to deteriorate. These nerves are required for voluntary muscle activity control. Neuronal loss leads to progressive muscle weakness that makes it difficult for one to move and function normally. These devastating consequences make SMA the leading genetic killer of infants, who succumb to the effects of the condition within a few years.Continue reading
Nicotine stresses you out!
By Caitlin Davies
Every day in Malta, one person will die from a smoking-related illness. People usually begin smoking tobacco in their adolescence and addiction quickly follows. Quitting is hard and the majority are unsuccessful. Nicotine, with its crippling withdrawal symptoms, is to blame. Research suggests this component of tobacco can be more addictive than heroin. Smokers say that nicotine is pleasurable and enables them to concentrate and reduce their anxiety. Scientists think the opposite.Continue reading
New designs for better streets
By Dr Antoine Zammit
Urban development in Malta has undergone an exponential growth in the past decades. This is a growth that has often been imposed indiscriminately within long-established and tightly knit streets, and worsened by a lack of urban design approaches by investors and politicians alike. The Maltese planning system has only reacted to economic and market conditions instead of trying to foresee them, and consecutive governments have simply sought to stimulate the construction industry further. In addition, none of the policies produced by the Malta Environment and Planning Authority (MEPA) have to date been urban design-oriented. The planning system has been overloaded with a plethora of policies that however fail to consider the street—arguably the most important spatial scale within the Maltese urban environment.Continue reading