Time, Space, & the Ocean Wanders
As an archipelago, the Maltese Islands have been a hotspot for seabird nesting since time immemorial. Marie Claire Gatt talks about her research and a major EU project determining how to protect far travelling seabirds. Photography by Jean Claude Vancell.
Art for research’s sake
Performing artists support medical research through the University of Malta’s Research, Innovation and Development Trust
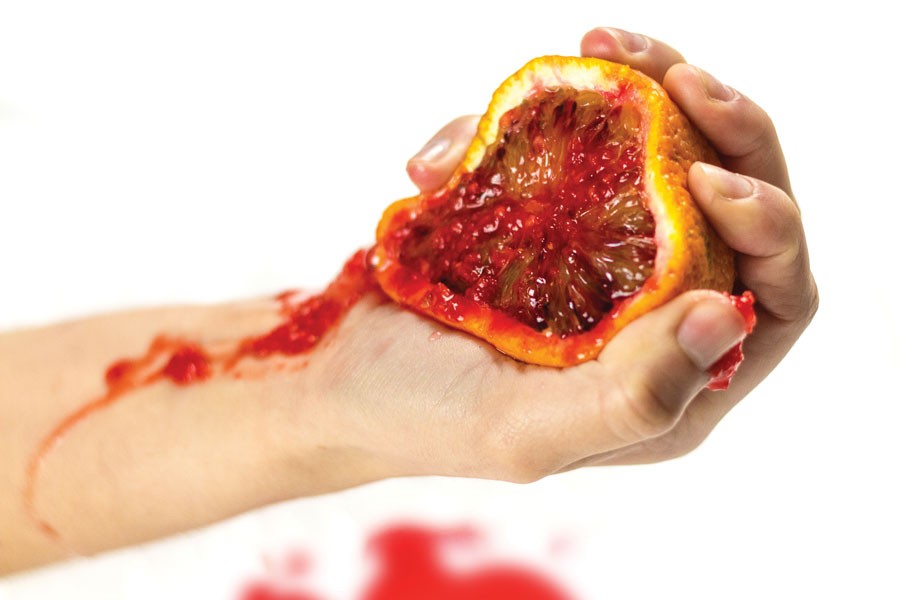
Who owns you?
One fifth of human genes have already been claimed as US Intellectual Property. But should anyone own our genes? And what happens when gene ownership can drastically prevent the advancement of life-saving cures?
The US Patent Office’s most controversial patents are on BRCA1 and BRCA2, both linked to the high risks of ovarian and breast cancer. They are now owned by Myriad Genetic Laboratories. In 1996, Myriad Genetics developed and began marketing a predictive test for the presence of possible cancer-causing mutations: the ‘BRCAnalysis’ test. The price of the test was US$3,000 but the company promised that it would eventually drop the price to US$300. This never happened because its patent holder had the right to stop any other party from duplicating the patented sequences. This single test accounted for over 80% of Myriad Genetics’ multibillion dollar business.
In 2009, the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) decided to challenge the patenting of human genes on legal grounds. The ACLU was the representative of 20 medial organisations, geneticists, women’s health groups, and patients unable to be screened due to the prohibitive patents. The ACLU’s position was that Myriad’s patents violated the patent law on the issue of patent-eligibility.
The case went before the Supreme Court. By 3 June, 2013 it was declared that the Myriad patents were invalid because they did not create or alter any of the genetic information encoded in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. The location and order of the nucleotides existed in nature before Myriad found them. The company simply discovered what was already there and did not create anything new.
There is no worldwide consensus on whether parts of the human genome should be granted intellectual property protection. The Myriad patents should alert us to the injustice of having a pharmaceutical company make money out of cancer predictive tests that could cost 10 times less than what is charged. The same patents stifled diagnostic testing and research that could have led to cures as well as limiting women’s options regarding their medical care in Malta as in all other parts of the world. There are various international and regional agreements that have described the human genome as being part of humanity’s ‘common heritage’, including the 1998 UN Declaration on the Human Genome and Human Rights. The Myriad patents controversy has shown that gene patenting does not work to stimulate more research—one of the prime arguments Big Pharma uses. It is time to explore other avenues that will both promote scientific progress and technological development but at the same time protect the special nature of human genes that make us who we are. No one should own our genes—they should be exploited in the interest of everyone.
Written by: Dr Jean Buttigieg
The Hidden History of the Maltese Genome
By reading someone’s DNA one can tell how likely they are to develop a disease or whether they are related to the person sitting next to them. By reading a nation’s DNA one can understand why a population is more likely to develop a disease or how a population came to exist. Scott Wilcockson talks to Prof. Alex Felice, Dr Joseph Borg, and Clint Mizzi (University of Malta) about their latest project that aims to sequence the Maltese genome and what it might reveal about the origins and health of the Maltese people.
Systematic Failure, Persistence and Success – A Table of Early School Leavers
In Europe, around one in 10 students (18-24 years old) is an ‘early school leaver’. For Malta, it is one in five. A fifth of our local student population is neither in school, nor in training, and with less than five SEC exams under their belt, Malta’s public education investment (~6% GDP) is not seeing much fruit. Cassi Camilleri speaks to Prof. Carmel Borg about what is needed to abandon the antiquated system our communities are being marred by. Photography by Elisa von Brockdorff.
Heartbreakers
Every person possesses the same genes within every cell. Their DNA provides the information to first create an entire functioning body and then keep it running. While all humans share more than 99.9% of their DNA, it is the subtle differences in our DNA that ensure individuality. Many differences are superficial effects, like hair colour, but some can have disastrous health effects. Scott Wilcockson talks to Dr Stephanie Bezzina-Wettinger (Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Malta) about her research on these subtle differences and how they can contribute to heart attacks.
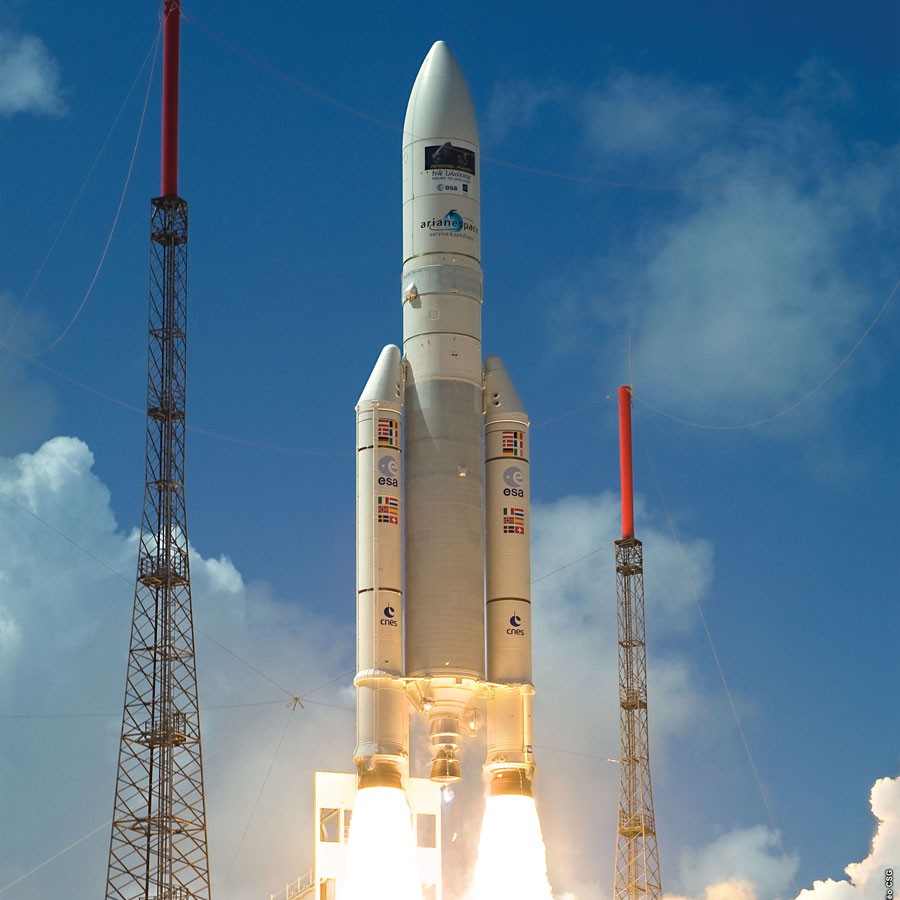
Rockets that Fail Safely
Spacecraft failures are spectacular. These unfortunate events are seared into the public memory. One reason why rockets can fail are software bugs. If a rocket’s computer system fails, that infamous blue screen leads to lost work hours, billions of Euro, and lives. Researchers from the Faculty of ICT and Faculty of Engineering (University of Malta) tell THINK about their collaboration with the European Space Agency (ESA) to test novel satellite software architecture to prevent rocket failure.
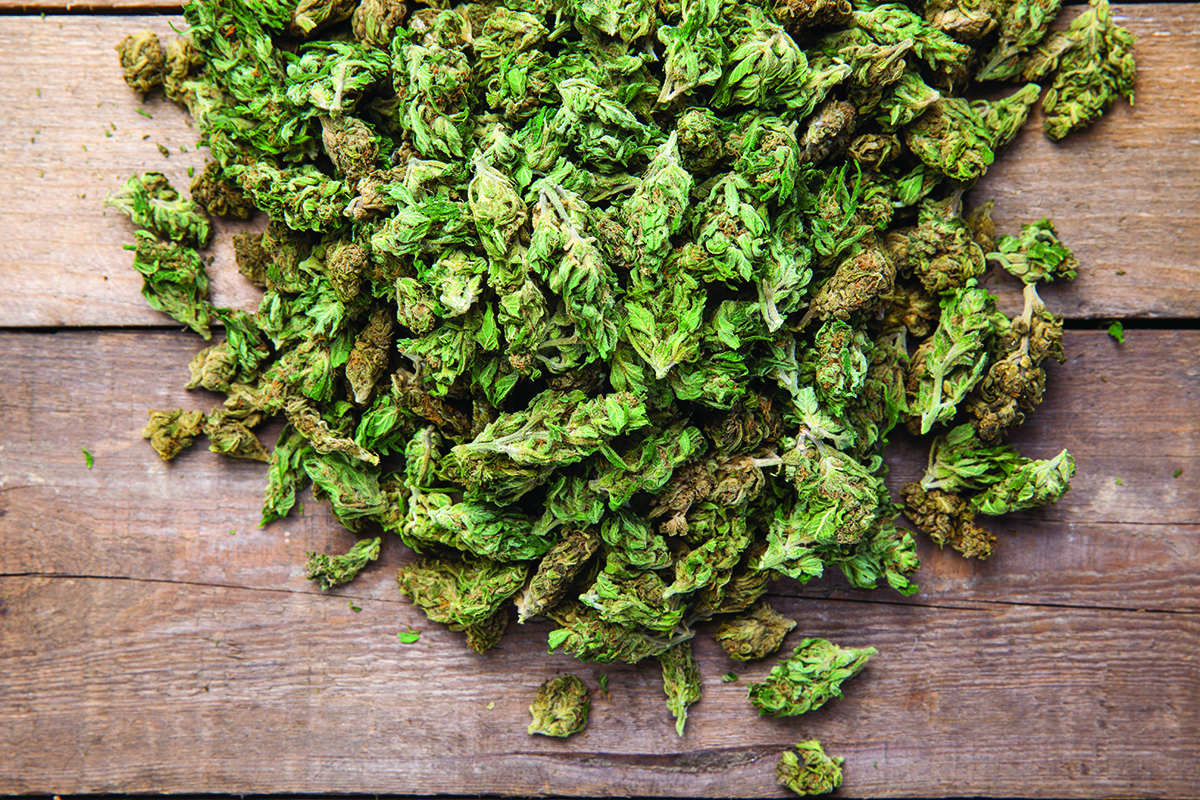
Marijuana for Epilepsy
Over the last few decades researchers have been unravelling the truth behind marijuana. Prof. Giuseppe Di Giovanni tells us more about its use in medical research.
Continue readingBeyond Lab Coats and Microscopes
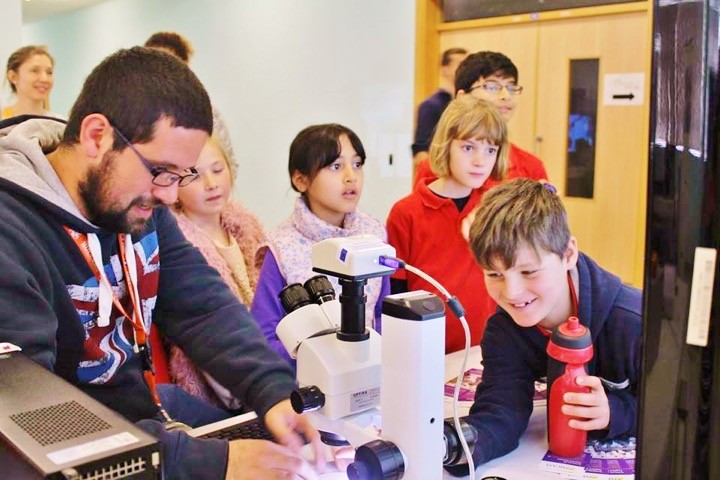
 Pride. That’s what Enrico felt when his name was announced at the Science Expo as the winner of the NSTF Contest for young scientists. The contest is a first step helping to build what Enrico Zammit Lonardelli calls his ‘scientific character’. It is a journey that led him to compete on an international level in Milan to represent Malta, meet and talk to incredible people, and learn about the way in which science is carried out all over the world. Feelings of honour, fulfilment, and success quickly followed. ‘Being surrounded by the best people in Europe in all possible aspects and fields of science was simply amazing.’
Pride. That’s what Enrico felt when his name was announced at the Science Expo as the winner of the NSTF Contest for young scientists. The contest is a first step helping to build what Enrico Zammit Lonardelli calls his ‘scientific character’. It is a journey that led him to compete on an international level in Milan to represent Malta, meet and talk to incredible people, and learn about the way in which science is carried out all over the world. Feelings of honour, fulfilment, and success quickly followed. ‘Being surrounded by the best people in Europe in all possible aspects and fields of science was simply amazing.’
Taking on such challenges in the scientific world at only 17, Zammit is the younger mirror image of another 17 year old that, around 20 years earlier, started the same journey. Today lecturer Conrad Attard (Faculty of ICT, University of Malta; Vice Chair, IEEE Malta Section) is handling several activities, one of which is an exhibit with his team for the same Science Expo which started Enrico off on his scientific voyage.
 Attard sees the Expo as a great way to distribute resources, and meet kids and visitors. ‘I want students to get excited about science and for more students to engage with these subjects’. That’s why Attard always teaches them in a fun way, by creating games were students need to solve logic problems that involve science and computing to learn and achieve their goals, and that is exactly what his exhibit at the NSTF Expo does.
Attard sees the Expo as a great way to distribute resources, and meet kids and visitors. ‘I want students to get excited about science and for more students to engage with these subjects’. That’s why Attard always teaches them in a fun way, by creating games were students need to solve logic problems that involve science and computing to learn and achieve their goals, and that is exactly what his exhibit at the NSTF Expo does.
So why is the growth of science communication important in Malta? For Attard, it is all about helping people find out what they do well in and pushing students to reach out beyond their comfort zone and that mistakes are part of the learning experience.
Zammit understands this principle. Some of his family members suffer from asthma motivating him to research it for the NSTF Expo. ‘Slowly I managed to understand the mechanism and a few questions popped into my mind. The following process was turning those questions into a project by research, planning, and finally experimentation.’
By favouring the multidisciplinary approach students are not limited to only becoming developers, but can also tackle related problems requiring knowledge or skills from other disciplines. This is what attracted Attard to the NSTF Science Expo as it uses crafts, different skills, and logic to solve problems.
 According to Zammit, the NSTF Expo and Programmes focus on analytical skills, public speaking, problem solving techniques, planning, critical thinking, creativity, and descriptive writing. ‘They all focus on character development rather than just the activity and provide an ensemble of quality development which is simply impossible to match by reading books and studying’. And, of course, there are amazing prizes.
According to Zammit, the NSTF Expo and Programmes focus on analytical skills, public speaking, problem solving techniques, planning, critical thinking, creativity, and descriptive writing. ‘They all focus on character development rather than just the activity and provide an ensemble of quality development which is simply impossible to match by reading books and studying’. And, of course, there are amazing prizes.
The Expo gave Zammit a platform for his work to be recognised by experts. ‘It has since motivated me to work harder because now I know what it feels like to win and create something useful. I want to repeat this success, hopefully at larger scales with ever bigger projects and aims.’
Maybe one day, it will be Zammit who will find himself teaching young students about science at the NSTF Expo.
The next NSTF Science Expo will be from 9–16 March for school visits, while the open weekend for everybody else will be on the 12–13 March.
For more information visit the NSTF Malta website or Facebook page.