URNA is Malta’s response to the 5th edition of the London Design Biennale 2025. THINK speaks to curator Andrew Borg Wirth and Arts Council Malta Internationalisation Executive Romina Delia to learn how this project seeks to create a connection between souls when experiencing a loss.
Continue readingIs BIM the solution to Malta’s Construction Woes?
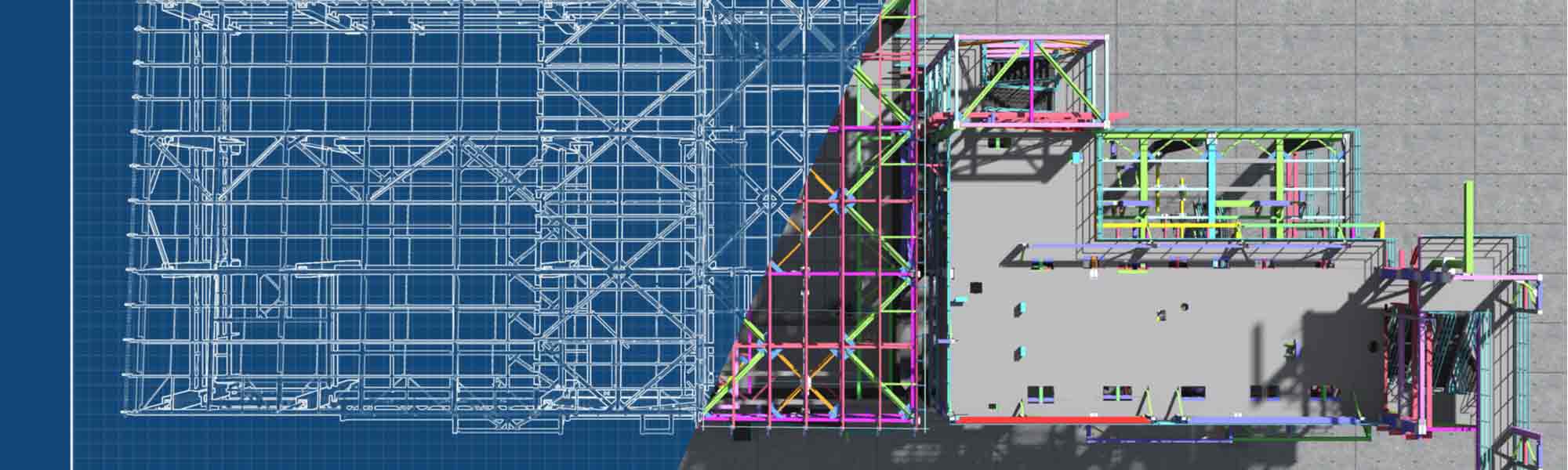
While the construction industry in Malta is facing many challenges, Building Information Modeling (BIM), is rising globally. Can BIM become the solution to Malta’s construction challenges?
Continue readingPeeling Away the Layers of Time
THINK takes a trip to explore research and archaeological work taking place at Borġ in-Nadur, overseen by Heritage Malta, which will see the Neolithic site freed from modern-day debris and accumulated material to show the original prehistoric structure in all its glory.
Continue readingArchitecture: A dying art?
Making smart choices for our current urban fabric through architecture requires a massive understanding of all the moving parts of the industry. But is it time to go back to basics? Cassi Camilleri speaks to Prof. Antonio Mollicone and the talented people at AP Valletta to come up with an answer.
The changes in the Maltese landscape over recent years has been drastic. All over social media, petitions keep being shared to prevent one original building or another from being torn down and replaced with contemporary apartments. This has ‘resulted in discomfort for many,’ says Prof. Antonio Mollicone, an architect lecturing within the Faculty of Built Environment (University of Malta).

The discomfort is multifaceted. On one level, it has to do with the physical climate within buildings. Over the last few decades, Malta has seen a shift in the property types people buy, and these properties seem to be leaving people hot or cold in their own homes.
Through his research, which used an old Maltese farmhouse as his case study, Mollicone found that ‘a property’s orientation, double skin (having two layers of brick walls), ceiling height and window measurements all have a role to play.’ Mollicone points out that ‘orientation is most important.’ In an ideal world, based on Malta’s position on the globe, ‘houses should be north-south facing and rotated clockwise to east by eight degrees to get the best of the sun in winter and the least of it in summer.’ Higher ceilings can create a four-degree difference in the temperature inside a room. As for the floor to ceiling windows you see in all the glossy magazines, Mollicone finds them problematic, noting the costs involved in terms of energy efficiency when replacing stone with glass. ‘Certain basic techniques in design are being lost in the fast-paced world of today,’ Mollicone asserts.

On this note, founding partner of AP Valletta, Konrad Buhagiar, says that with the ‘era of radical pragmatism’ we are currently living in, ‘the commercial aspect of a project is paramount,’ adding, ‘It will always be so. It is the nature of the industry.’ But with this being said, effort needs to be put into giving buildings and new projects a depth that ‘connects [them] to [their] context.’
Even with the best of intentions, challenges still arise. Mollicone laments the flashy features he sees added to a building’s façade before a thought is given to function. ‘It’s make-up for buildings. Nothing more. I call it lipstick architecture.’
Luca Caruso, an environmental architect at AP, also speaks frankly, noting that the ‘construction sector is the least innovative worldwide.’ However, by putting an emphasis on quality and criticism, this can change. ‘Criticism is important in order to raise awareness about the possible consequences of Malta’s ‘uncontrolled’ growth. […] Debate can lead to new, innovative ways to inspire decision-makers while respecting local characteristics.’
The reality, as Caruso states, is that ‘Malta has undergone massive changes over the last 30 years, and this is a process that requires some more years to mature.’ Buhagiar announces himself a cynic, saying that ‘to produce something excellent, you need an enormous amount of thought and discipline, rigour, and dare I say, sacrifice, all words that do not describe the current culture in any way.’ But Mollicone has hope that common sense will prevail. ‘All we need is to take more time to think about things. Create mindfully. That’s all.’
Cultural Regeneration through Urban Spaces and Places
The effects of a European Capital of Culture are felt through both the cultural activities that take place and through the interactions people have with each other as well as the space around them in their everyday lives.
The Valletta 2018 Foundation has been working tirelessly on several projects preparing Valletta for its title as European Capital of Culture in Malta in 2018. More so, it is researching how these projects are changing the lives of people.
These interactions between communities and their surrounding space are key issues being investigated by the Valletta 2018 Evaluation & Monitoring research process. This is a five-year research study examining the impacts of the European Capital of Culture on Malta’s society and economy.
Dr Antoine Zammit, with the Valletta 2018 Foundation, has been studying the relationship between community inclusion and space in cultural infrastructural projects. His research focuses on four specific infrastructural projects taking place in Valletta as part of the European Capital of Culture: The Valletta Design Cluster (il-Biċċerija) and its surrounding neighbourhood; Strait Street; the relocation of MUŻA – Mużew Nazzjonali tal-Arti (Malta’s National Museum of Fine Arts) – to Auberge d’Italie and Pjazza de Valette; and the area surrounding the Valletta Covered Market (is-Suq tal-Belt).
The four projects are in different stages of their implementation, and have been dispersed throughout Valletta in a way that allows them to collide with many of the different districts of the capital. While none lack cultural significance, each project has displayed different strengths in implementation. The Valletta Market and Strait Street Projects have a particularly strong commercial value, while the Valletta Design Cluster is aimed at creative design and encouraging entreprenuership. MUŻA, more overtly than any of the other three projects, is an attempt at traditional forms of cultural engagement and regeneration through the development of a national, community-driven musuem of art. Zammit, together with two M.Arch. (Architecture and Urban Design) students—Daniel Attard and Christopher Azzopardi—carried out extensive studies to gain a deeper understanding of the sites.
“Quality urban design has increasingly become about creating these habitable places. It is ultimately all about the quality of life of residents.”
Attard developed a matrix in order to score the different types of interactions within each site. Split into categories such as ‘aural’, ‘user categories’ and ‘actual use of space,’ the sections help identify emerging patterns and traits from the implementations of the projects. The Biċċerija and Strait Street all score high in the ‘aural’ category, meaning various elements that contributed to noise, or the lack of it, were observed. MUŻA and the Covered Market both qualified for the ‘user categories’ section, meaning that a relatively diverse demographic was observed making use of the place. The Valletta Design Cluster was noted for having a higher level of human interaction take place daily (balcony conversations, loud conversations in general, and so on). Finally, all four sites qualified for the category of ‘actual use of space,’ meaning that people actively show awareness of the space by taking photos, complaining due to lack of public conveniences, construction work, and shops setting up or closing down, among other things.
On the other hand, Azzopardi focused on the spatial quality of the sites by looking at their accessibility and permeability, perception and comfort, and the vitality of the four sites. Of the four, Strait Street, more specifically the intersection with Old Theatre Street, scored highest, followed by MUŻA and the Valletta Market. The Valletta Design Cluster obtained the lowest score, suggesting that the site in its current state is poorly perceived and somewhat inaccessible. Matching Azzopardi’s findings with statistical data, obtained at a neighbourhood level through the NSO’s evaluation of the available 2011 Census Data, Zammit has determined some relationship (but not statistically significant), between the buildings’ current state of repair and the community’s achievements in literacy, education, and employment.
| Museum of the People |
|
Naqsam il-MUŻA is a branch project inspired by MUŻA. Currently in progress, participants in the Naqsam il-MUŻA project were selected from different communities around Malta and taken to see the art collection of the National Museum of Fine Arts. They will then exhibit their choice of artwork from the museum in their localities. It brings the museum to the people, rather than the other way round. |
The diversity of the four sites were key to Zammit’s studies. He studied the effect their differing cultural infrastructure had on the cultural regeneration of Valletta. ‘Cultural infrastructure entails those interventions, which generally have some kind of physical implication, in an urban space which tends to enhance and broaden people’s cultural appreciation,’ explains Dr Zammit, ‘but I see it as requiring an added value. In my opinion, art for art’s sake in these cases doesn’t mean anything. Which is why the question which I try to answer in my research is, “what will that infrastructure give back to the community at the end of it all?”’ Other research, similar to Zammit’s, holds that more than just creating spaces, cultural regenerative projects should aim to create places which result from quality urban design. ‘Over the past two years, I started to realise that the real difference is ‘between places that are alive, versus habitable places,’ comments Zammit, who thinks that, ‘quality urban design has increasingly become about creating these habitable places. It is ultimately all about the quality of life of residents.’ This issue of liveability is key to being a European Capital of Culture. Its goals are to create high-quality cultural and artistic activities while improving the quality of life of communities through culture. Zammit’s study highlights many potential issues such as an increase in noise pollution, gentrification resulting from a rise in property values and rental prices, and other potential impacts on Valletta residents. The Valletta 2018 Foundation is discussing these issues in its upcoming conference Cities as Community Spaces in November 2016, which will bring together a number of international speakers to explore how different communities make use of public spaces for creativity, contestation, and interaction.
For more: valletta2018.org