Eyes front!
How often do your date’s eyes glance down at your chest? Which products do people notice in a supermarket? How long does it take you to read a billboard?
Eye trackers are helping researchers around the world answer questions like these. From analysing user experience to developing a new generation of video games, this technology offers a novel way of interacting with machines. People with disabilities, for example, can use them to control computers. A team at the Department of Systems and Control Engineering (University of Malta) is using a research-grade eye-gaze tracker, worth around €40,000, to test technologies they are planning to commercialise soon.
Continue readingPushing for Malta’s industrial renaissance
With all the cranes strewn across the Maltese landscape, it appears that the construction industry is one of Malta’s primary economic drivers. But there are other, less polluting ways of generating income. Dr Ing. Marc Anthony Azzopardi discusses MEMENTO, the high-performance electronics project that could pave the way for a much-needed cultural shift in manufacturing.
Continue readingUp, up and away!
How do aerospace research engineers test new cockpit technologies without having to actually fly a plane Answer: flight simulators. These machines give pilots and engineers a safe, controlled environment in which to practise their flying and test out new technologies. In 2016 the team at the Institute of Aerospace Technologies at the University of Malta (IAT) started work on its first-ever flight simulator—SARAH (Simulator for Avionics Research and Aircraft HMI). Its outer shell was already available, having been constructed a few years back by Prof Carmel Pulé. From there, the team built the flight deck hardware and simulation software, and installed all the wiring as well as side sticks, pedals, a Flight Control Unit (FCU) and a central pedestal. The team constructing the simulator faced many hurdles. The biggest challenge was coordinating amongst everyone involved in the build: students, suppliers, and academic and technical staff. Careful planning was crucial.
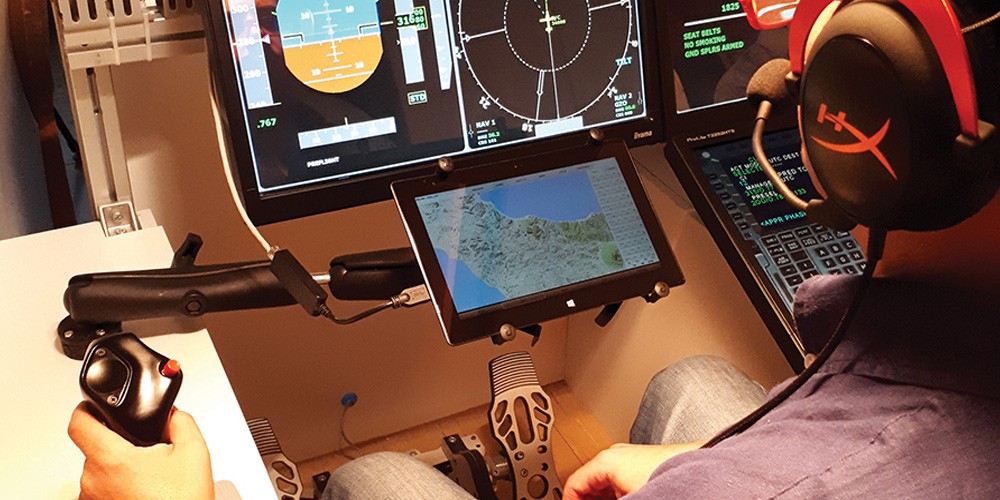

The result is a simulator representative of an Airbus aircraft. However, it can also be easily reconfigured to simulate other aircraft, making it ideal for research purposes and experimentation. The Instructor Operating Station (IOS) also makes it possible to select a departure airport and change weather conditions.
One of the first uses of SARAH was to conduct research on technology that enables pilots to interact with cockpit automation using touchscreen gestures and voice commands. This research was conducted as part of the TOUCH-FLIGHT 2 research and innovation project (read more about this in Issue 19).
Going beyond the original aim of SARAH being used for research purposes, the IAT is also using the technology to educate graduates and young children in the hope of sparking an interest in the field. Earlier this year, a group of secondary school students flew their own virtual planes under the guidance of a professional airline pilot.
Looking ahead, the IAT plans to incorporate more state-of-the-art equipment into SARAH to increase its capabilities and make the user experience even more realistic. There are also plans to build other simulators—including a full-motion flight simulator and an Air Traffic Control simulator—and to connect them together to simulate more complex scenarios involving pilots and air traffic controllers; a scenario that would more closely resemble the experience of a real airport.Project TOUCH-FLIGHT 2 was financed by the Malta Council for Science & Technology, for and on behalf of the Foundation for Science and Technology, through the FUSION: R&I Technology Development Programme.
Author: Abigail Galea
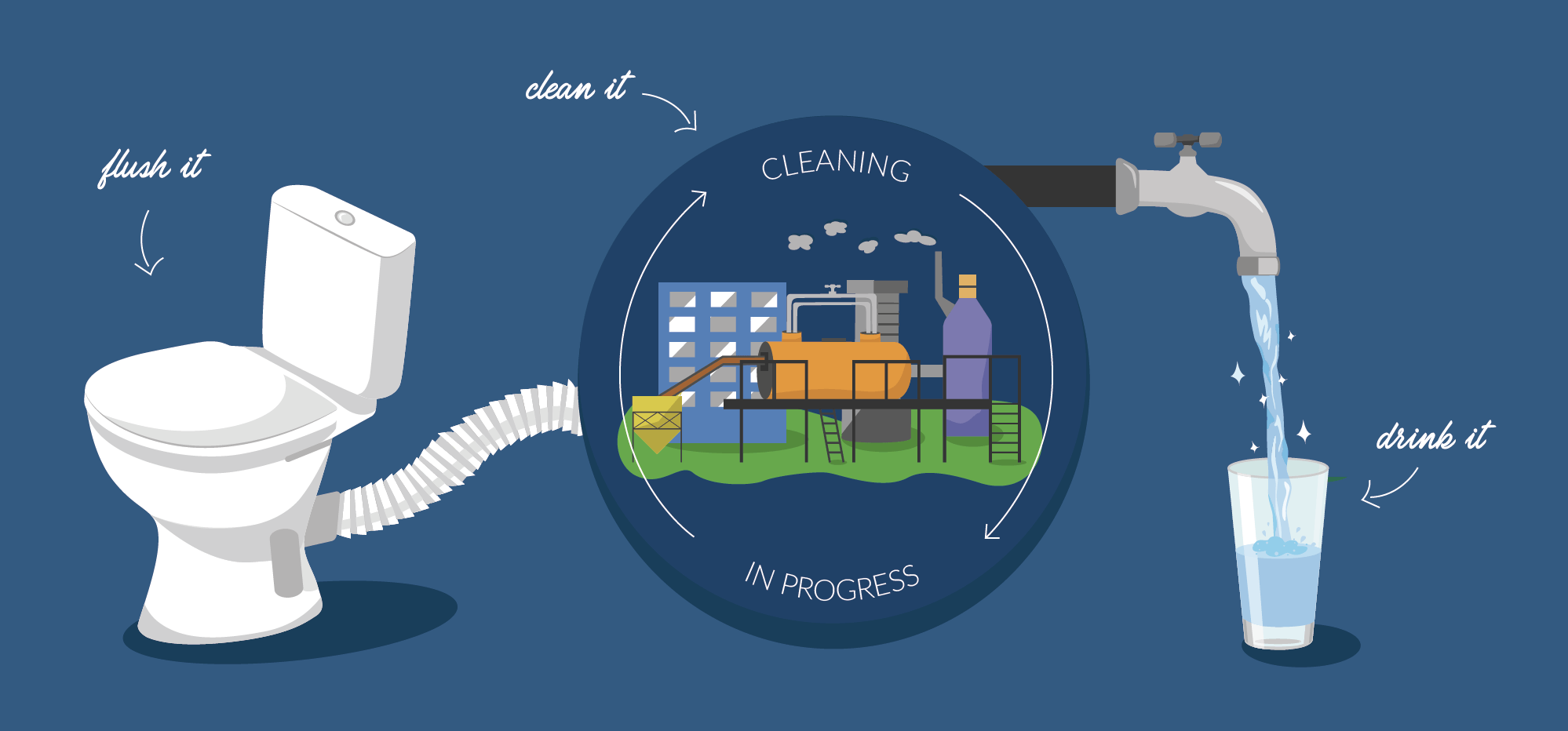
Sewage works
Water is our number one resource. It not only sustains life, but also supports the economy and its development. And yet, water is taken for granted. Kirsty Callan talks to Marco Cremona, the man behind the revolutionary water treatment solution that promised to reduce Maltese hotels’ water use by 85%.
Designing the factory of the future
With consumer demand reaching new highs, automation in industry is essential. Dr Ing. Emmanuel Francalanza writes about his contribution to streamlining the complex factory design process for contemporary engineers.
From smartphones, to smartwatches, smart cars to smart houses, intelligent technology is inescapable. Busier people have made efficiency a valuable currency and thus the ‘Internet of Things’ (IoT), and its plethora of connected devices, has become a necessary part of everyday life. The application of this model goes way beyond the regular consumer, however. Continue reading