Bursting the RRI bubble
Relationships are based on trust, communication, and mutual respect. The same can be said of Responsible Research and Innovation (RRI). Behind all the new ideas, it all boils down to a group of people, hailing from different walks of life, coming together to try and create a better future for everyone. At the fourth annual NUCLEUS conference, researchers, academics, science communicators, creatives, and business people flocked to the tiny isle of Malta to share their stories and attempts to embed RRI into their institutions and communities. As everyone settled in, dialogue flowed among delegates and the room was abuzz. University of Malta pro-rector Prof. Godfrey Baldacchino opened the conference with a question: How similar are universities and Valletta, the fortified capital that was hosting the conference? Having been constructed following Malta’s infamous Great Siege, the Knights encased Valletta in massive bastions, allowing only four small entry points. ‘Valletta is an island on an island,’ Baldacchino said. ‘Are universities the same? Are we trying to protect our own?’ The question had many heads nodding in response.
Most people in the room expressed a feeling of obligation to render knowledge more accessible, more relevant, and more digestible to a wider audience. But they encounter a myriad of challenges. Engaging with publics or policy makers isn’t easy. It means addressing different needs in different ways, sometimes even pandering to whims and flights of fancy. Most people noted issues with time, funding, and resources, calling for processes to be formalised. Others pointed to a lack of creative skills and, sometimes, general interest across the board. What also quickly emerged was frustration with the term RRI itself, creating confusion where there needn’t be any.

With all of these difficulties, however, came solutions. Dr Penny Haworth from the South African Institute for Aquatic Biodiversity, said that in her experience ‘we need to look at what universities are already doing and work smart. Win hearts and minds.’ University of Malta’s Nika Levikov also pointed out that ‘there are a lot of people practicing RRI who are not conscious of it.’ And for those who do not believe it to be a priority, for those who do not want to engage? ‘You have to set them aside and show them it is possible in a way they understand,’ says Zoran Marković from MISANU, Serbia.
Picking up Baldacchino’s thread on bringing down the walls of universities and research institutions, Dr Annette Klinkert from Rhine-Waal University of Applied Sciences in Germany summed up her main takeaway from all the discussions. ‘What we can learn here is that it’s time to burst the bubble in which we work. Especially this field of RRI. It is time to leave our cosy little community with our results.’ The results are the various projects that NUCLEUS has been championing over the past years, bringing research to its audiences. ‘All the projects are useless if they can’t merge and get out [into society and communities],’ she emphasises. ‘If they don’t merge, they’re pointless. It is time to burst the bubble.’
Author: Cassi Camilleri
Food, gender and climate change
Food is one of life’s constants. Yet, what we eat has major ramifications on global climate. Food production uses up major resources: it accounts for more than 70% of total freshwater use, over one-third of land use, and accounts for just shy of 25% of total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, of which 80% is livestock. Yes, that steak you just ate has had a direct impact on the world’s climate! There is something of an oxymoron in the world’s food ecosystems. Overconsumption is linked to major health problems like obesity, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers that together account for up to 71% of global deaths. On the other hand, there are around one billion people in the world who suffer from hunger and underconsumption. All of this is compounded by problems of food loss and waste. This raises important questions related to the ethics of worldwide food production and distribution.
Food production and consumption is determined by many factors: population numbers, incomes, globalisation, sex (biology), and gender (socio-cultural) differences. The combination of a sedentary lifestyle and an unbalanced diet, high in red, processed meat, low in fruits and vegetables, is a common problem in many developed countries. And this impacts not just human health, but also biodiversity and ecosystems.
Supervised by Prof Simone Borg, I chose an exploratory research design with embedded case studies. The aim was to analyse the dietary patterns of men and women. I wanted to critically question the power relations that feed into socio-economic inequities and lead to particular food choices. I used both quantitative and qualitative methods, modelling the life cycle assessment and scenario emission projections for 2050 in Malta, Brazil, Australia, India, and Zambia among males and females aged 16 to 64.

The four dietary scenarios I took into consideration were present-day consumption patterns (referring to the 2005/7 Food and Agriculture reference scenario), the World Health Organisation (WHO) recommended diet (300g of meat per week and five portions per day of fruit and veg), vegetarian/mediterranean/pescatarian diets, and the vegan diet. From there, I measured ammonia emissions, land use, and water from cradle to farm gate, with a special focus on gender.
The findings were alarming, indicating that none of the five countries are able to meet emissions reductions under current dietary patterns. If we were to adopt the WHO recommended diet, GHGEs would be cut by 31.2%. A better result would be gained from a vegetarian diet, which would slash emissions by 66%, while a vegan diet comes out on top with a projected 74% reduction.
Some interesting points that arose were that the Global Warming Potential is higher in men in all countries due to higher meat consumption. Zambia and India would benefit the most from the proposed dietary shifts in absolute terms, while Australia, Malta, and Brazil would feel the positive impacts on individual levels in per capita terms, reducing carbon footprints considerably.
Reduced meat consumption substantially lowers dietary GHG emissions. We need to prospectively consider the interplay of sex and gender, and develop climate change, health, and microeconomic policies for effective intervention and sustainable diets. Adopting a flexitarian diet that is mostly fruits and vegetables, with the occasional consumption of meat, can save lives, the planet, and economies—some food for thought!
This research was carried out as part of a Master of Science (Research) in Climate Change and Sustainable Development at the Institute of Climate Change and Sustainable Development, University of Malta.
Author: Precious Shola Mwamulima
The rise of the academic entrepreneur
What is it that separates innovation in the lab from successful multi-million euro ventures that make money and have a positive impact on the world? The Knowledge Transfer Office’s Andras Havasi writes.
Continue readingBlockchain: Not just bitcoin
Blockchain is still a big unknown, even for some professionals. Blockchain and the Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) have been made infamous by Bitcoin, a digital payment and peer-to-peer monetary transaction system that bypasses banks and third party endorsements. But DLT and the Blockchain protocol can be used for other purposes. Blockchain’s greatest strength lies in its decentralised architecture. It allows transactions to be shared openly across independent nodes, verified by encrypted checksums that give each closed block a distinct, indelible signature. All these connected transactions, chained within a common system, make tampering practically impossible. Blockchain is irrevocable, affordable, flexible, and secure.
But what about other applications of these concepts. What if we were to apply such technology to every data exchange? Data and information in the digital age is spearheading the evolution of services and product development, serving a continuum of user demands at all levels and scales, boosting research and innovation applications. Indeed, data is nowadays considered a key ingredient for competitiveness, and this is not about to change anytime soon.

The greatest bottleneck is data sharing. Data production is growing and covering many realms but unfortunately most of it remains locked up in closed databases, enterprises, and institutions. Unofficially it is estimated that the world generates 16 zettabytes of data annually (that’s 16 billion terabyte laptops), but only 1% is analysed. The problem is that data is withheld by data collectors who consider data hoarding to be a right. Where data is released it does not usually flow to users. As a result, we now have institutions running massive centralised databases, often conducting data archaeology, compiling it at local, regional, and global scales. They address the needs of different user groups, but they also impose licensing procedures that ultimately restrain the power of free data flows, establishing unnecessary monopolies.
Blockchain can unleash the full power of data by providing a system for seamless, efficient and secure data transactions. It can lead to so many applications, such as eliminating the need for shipping documents in the transportation of goods, and making the freight and logistics industry more time and cost efficient. Data could be funnelled into artificial intelligence systems to create high performance human-machine interfaces, self-automated robots, cars, and ships. These devices, with information from big data, would be able to learn from their mistakes and autonomously adapt to changing environments. In medicine, large data sets would prove priceless in drug and treatment design, doing away with the constraints of limited sample sizes. The application of such technologies is limited only by our own imagination.
A new digital revolution is looming ahead. Are we ready to be amongst the first to take this leap into the future?
Author: Prof. Aldo Drago
The Maltese Time Machine: Magna Żmien
As I write this article, a box full of 8mm film has just been delivered to our studio. On these tapes is local home footage featuring carnival celebrations from the 1960s, a visit by the UK’s Queen Elizabeth II, and an assorted series of family events recorded around the Maltese Islands. These films are valuable historical records opening a window onto the unfiltered and uncensored perspective of Maltese citizens. Magna Żmien is a Valletta 2018 project coordinated by artistic director Andrew Alamango and a collective of like-minded individuals. The purpose of the project is to collect and preserve historic Maltese content recorded on home sound, image, and video equipment over the past century. Left neglected, these personal documents containing evidence of Malta’s changing landscapes—physical, social, and political—might have been lost and forgotten. Instead, the team is reusing them, reinterpreting them through art.
The move to digitise and make available fading analogue memories is physically manifested through ‘The Magnificent Memory Machine’—the Kapsula Merill, designed and built by Matthew Pandolfino, Andre Vujicic and Late Interactive. In the driver’s seat is Armchair Voyager Wistin (Jacob Piccinino). Behind the scenes is the professional studio that makes it all happen, digitising open reel tapes, audio cassettes, vinyl, Super 8 and 8mm film, photographs, negatives, and slides at high resolution. Since February 2018, we have digitised over 2,000 items from 51 different donors, in addition to receiving a further 600 digital files from private collections.
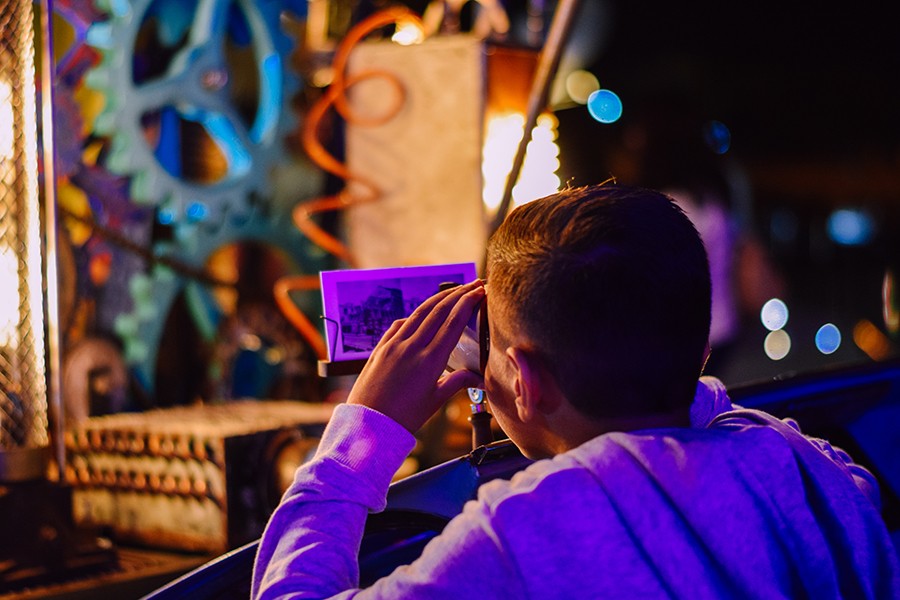

The collected material has many stories to tell. Our performance events throughout 2018, including at Science and the City and Malta Café Scientifique, only scratch the surface when it comes to the sheer volume of material we have been allowed to copy by donors.
One thing we often encounter is the personal voice message—greetings between diasporic Maltese. Dating back to the 1950s, these appear most frequently on open reel and audio cassette tape, but also on special vinyl discs. One particular recording is by a man named Charlie who recorded his message in a Calibre booth on a platform at London Waterloo station. In the message, Charlie sends wishes to his family and regales them with tales of all the football matches he is attending, one of which he is particularly excited about: England vs East Germany. Some minor detective work has revealed that this recording was made on 24 November 1970 when England beat East Germany three goals to one.
Messages such as these may seem inconsequential, but of all the voice recordings we have heard, they are perhaps among the most honest. Recorded in a busy, alien environment under strict time constraints, the speakers didn’t have the luxury of retakes before their voices were forever fixed on vinyl.
Magna Żmien will continue to collect sounds, images, and videos like these, and present its research in innovative contexts beyond 2018. We want to continue engaging citizens in the technical and cultural components at the heart of our project. Agreements are also underway to establish a formal association between Magna Żmien and the National Archives, ensuring the longevity of this material as public documents are accessible to all. What we collect, after all, belongs to the Maltese people at home and abroad. The recordings contain an essence of our national identity that cannot and should not be lost.
For more, visit: www.magnazmien.com
Author: Andrew Pace for the Valletta 2018 Foundation
Pushing for Malta’s industrial renaissance
With all the cranes strewn across the Maltese landscape, it appears that the construction industry is one of Malta’s primary economic drivers. But there are other, less polluting ways of generating income. Dr Ing. Marc Anthony Azzopardi discusses MEMENTO, the high-performance electronics project that could pave the way for a much-needed cultural shift in manufacturing.
Continue readingThe Bible in stone
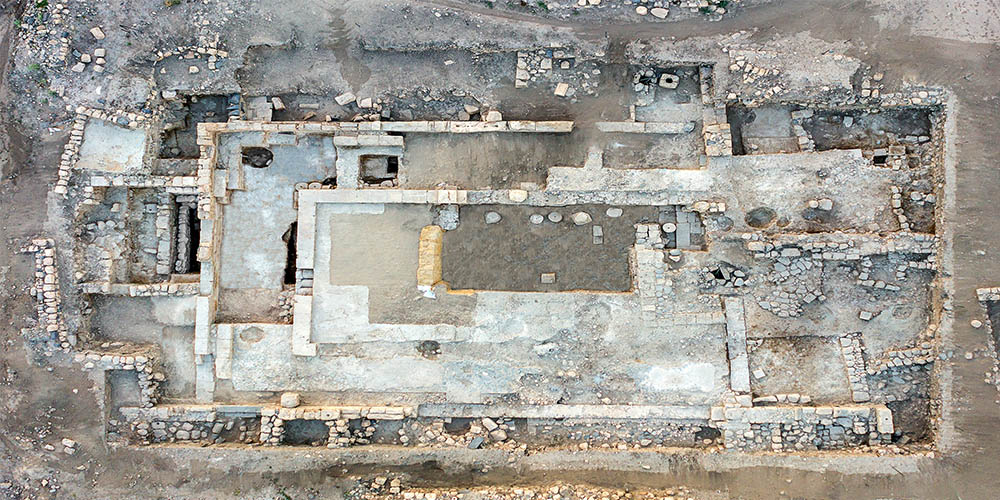
Excavations of an ancient synagogue at Huqoq, Israel
Buried inside an unassuming hill in Israel’s Lower Galilee is a magnificent ancient synagogue with splendid mosaic panels that have been hidden away for over 1,400 years. Dr Dennis Mizzi writes about the project that is bringing them to light.
Continue readingCan the EU empower women in Afghanistan
The European Union’s success relies on positive relationships—cooperation and good will is key. The EU’s Development and Cooperation Policy exists to support these connections. Its focus is on external relations, establishing partnerships with developing countries and channelling billions of euros to them every year. The European Commission plays a crucial role in this regard, managing and implementing directives on behalf of the EU. But what do we really know about the effectiveness of EU aid in helping citizens in developing countries? And how far is female empowerment part of this agenda?
In short—we don’t know much!
Research in this area is scarce, and this is what prompted me to tackle this question myself, under the supervision of Dr Stefano Moncada. My specific focus was on assessing whether the EU is committed to gender equality and female empowerment, taking Afghanistan as a case study. I reviewed all the available aid programming documents from the last financial period, and assessed whether the EU was effectively supporting Afghanistan to achieve the fifth Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) of gender equality. I adopted a mixed-method approach, using content analysis and descriptive statistics. Basically, this meant coming up with a very long list of keywords related to gender, and checking how many times these words appeared in the policy documents. Whoever invented the ‘ctrl + F’ function saved my academic life!

The results of my research were pretty surprising. I found that the EU is now focusing much more on gender empowerment on the ground in Afghanistan than it did a few years ago.
According to my data, and when comparing this to previous studies, it appears that the EU’s commitment to supporting this goal is growing over time. However, I also found that there is substantial room for improvement, as the attention given to such issues is rather conservative, and not equally balanced across all the SDG targets. For example, the need to increase women’s employment is mentioned many more times than the need to support female education or political participation. This is surprising as education is key to many other improvements in wellbeing. Nevertheless, I believe the overall results are encouraging and important, not only to highlight improvements in the effectiveness of the EU’s development and cooperation policy, but also in reply to a growing sentiment that puts into question the EU’s capacity to manage, and lead, in key policy areas. We can only hope that this continues exponentially.
This research was carried out as part of a Bachelor of European Studies (Honours) at the Institute for European Studies, University of Malta. The dissertation received the ‘2018 Best Dissertation Award’.