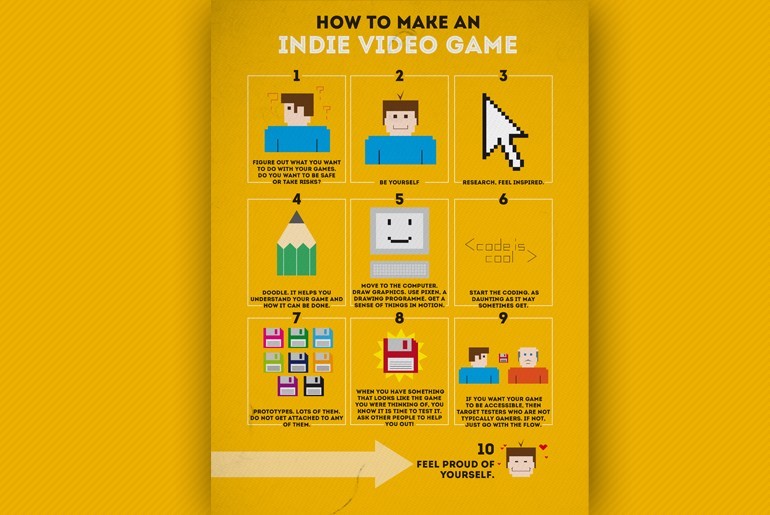
In each creative act, a personal price is paid. When the project you have been working on so hard falls to pieces because of funding, it is hard to accept its demise. The feeling of failure, betrayal, and loneliness is an easy trap to fall into. This is the independent game maker’s industry: a bloodthirsty world rife with competition, sucking pockets dry from the very beginning of the creative process.
Maltese game makers face a harsher reality. Not all game makers are lucky enough to make it to the finish line, publish, and make good money. Rather, most of them rarely do. Yet, if and when they get there, it is often thanks to the passion and dedication they put into their creation — together with the continuous support of others.
Dr Pippin Barr always had a passion for making things, be it playing with blocks or doodling. His time lecturing at the Center for Computer Game Research at the IT University of Copenhagen, together with his recent team-up with the newly opened Institute of Digital Games at the University of Malta, only served to reincarnate another form of this passion: Pippin makes games. At the Museum of Modern Art in New York he exhibited his most well known work: the game rendition of Marina Abramović’s The Artist is Present. He thought of the idea while planning to deliver lectures about how artists invoke emotions through laborious means in their artworks. In The Artist is Present, artist Marina Abramović sits still in front of hundreds of thousands of people and just stares into their eyes for as long as participants desire.
There is more to this performance than meets the eye. Beyond the simplistic façade, Barr saw real depth. Through eye contact, the artist and audience forge a unique connection. All barriers drop, and human emotion flows with a great rawness that games are so ‘awful’ at embodying. Yet, paradoxically, there is a militariness in the preparation behind the performance that games embrace only too well. Not only does the artist have to physically programme herself to withstand over 700 hours’ worth of performing, but the audience also prepares for the experience in their own way, by disciplining themselves as they patiently wait for their turn.
“It’s a pretty lonely road and it can be tough when you’re stuck with yourself”
Pippin Barr
‘Good research is, after all, creative,’ according to Pippin Barr. By combining his academic background with his creative impulse, he made an art game — a marriage between art and video games. These are games about games, which test their values and limits. Barr relishes the very idea of questioning the way things work. His self-reflexive games serve as a platform for him to call into question life’s so-called certainties, in a way that is powerful enough to strike a chord in both himself and the player. He is looking to create a deep emotional resonance, which gives the player a chance to ‘get’ the game through a unique personal experience. Sometimes, players write about his games and capture what Pippin Barr was thinking about, as he put it, ‘better than I could myself’, or read deeper than his own thoughts.
As far as gameplay goes, The Artist is Present is fairly easy to manoeuvre in. The look is fully pixellated yet captures the ambience at the Museum. The first screen of the game places the player in front of its doors and you are only allowed in if you are playing the game during the actual exhibition’s opening hours in America. Until then, there is no option but to wait till around 4:30 pm our time (GMT+1). The frustration continues increasing since after entering you will still have to wait behind a long queue of strangers to experience the performance work. This reflects real world participants who had to wait to experience The Artist is Present. If they were lucky, they sat in front of the artist and gazed at her for as long as they wanted.
Interestingly, Marina Abramović also played the game. She told Barr about how she was kicked out of the queue when she tried to catch a quick lunch in the real world as she was queuing in the digital one. Very unlucky, but the trick is to keep the game tab open. Other than that, good luck!
Despite that little hiccup, Abramović did not give up on the concept of digitalising the experience of her art. After The Artist is Present, Barr and Abramović set forth on a new quest: the making of the Digital Marina Abramović Institute. Released last October, it has proven to be a great challenge for those who cannot help but switch windows to check up on their Facebook notifications – not only are the instructions in a scrolling marquee, but you have to keep pressing the Shift button on your keyboard to prove you are awake and aware of what is happening in the game. It is the same kind of awareness that is expected out of the physical experience of the real-life Institute.
The quirkiness of Barr’s games reflects their creator. Besides The Artist is Present, in Let’s Play: Ancient Greek Punishment, he adapted a Greek Sisyphus myth to experiment with the frustration of not being rewarded. In Mumble Indie Bungle, he toyed with the cultural background of indie game bundles by creating ‘terrible’ versions with ‘misheard titles’ (and so, ‘misheard’ game concepts) of renowned indie games. One of his 2013 projects involves the creation of an iPhone game, called Snek, an adaptation of the good old Nokia 3310 Snake. In his version, Pippin Barr turned the effect of the smooth ‘naturally’ perfect touch interface of the device upon its head, by using the gyroscope feature. Instead, the interaction with the Apple device becomes thoroughly awkward, as the player has to move around very unnaturally because of the requirements of the game.
This dedicated passion for challenging boundaries ultimately drives creators and artists alike to step out of their comfort zone and make things. These things challenge the way society thinks and its value systems. Game making is no exception, especially for independent developers. An artist yearns for the satisfaction that comes with following a creative impulse and succeeding. In Barr’s case, being ‘part of the movement to expand game boundaries and show players (and ourselves) that the possibilities for what might be “allowed” in games is extremely broad.’
Accomplishing so much, against the culture industry’s odds, is a great triumph for most indie developers. For Pippin Barr, the real moment of success is when the game is finished and is being played. Then he knows that someone sat with the game and actually had an experience — maybe even ‘got it’.
Follow Pippin Barr on Twitter: @pippinbarr or on: www.pippinbarr.com
Giuliana Barbaro-Sant is part of the Department of English Master of Arts programme.