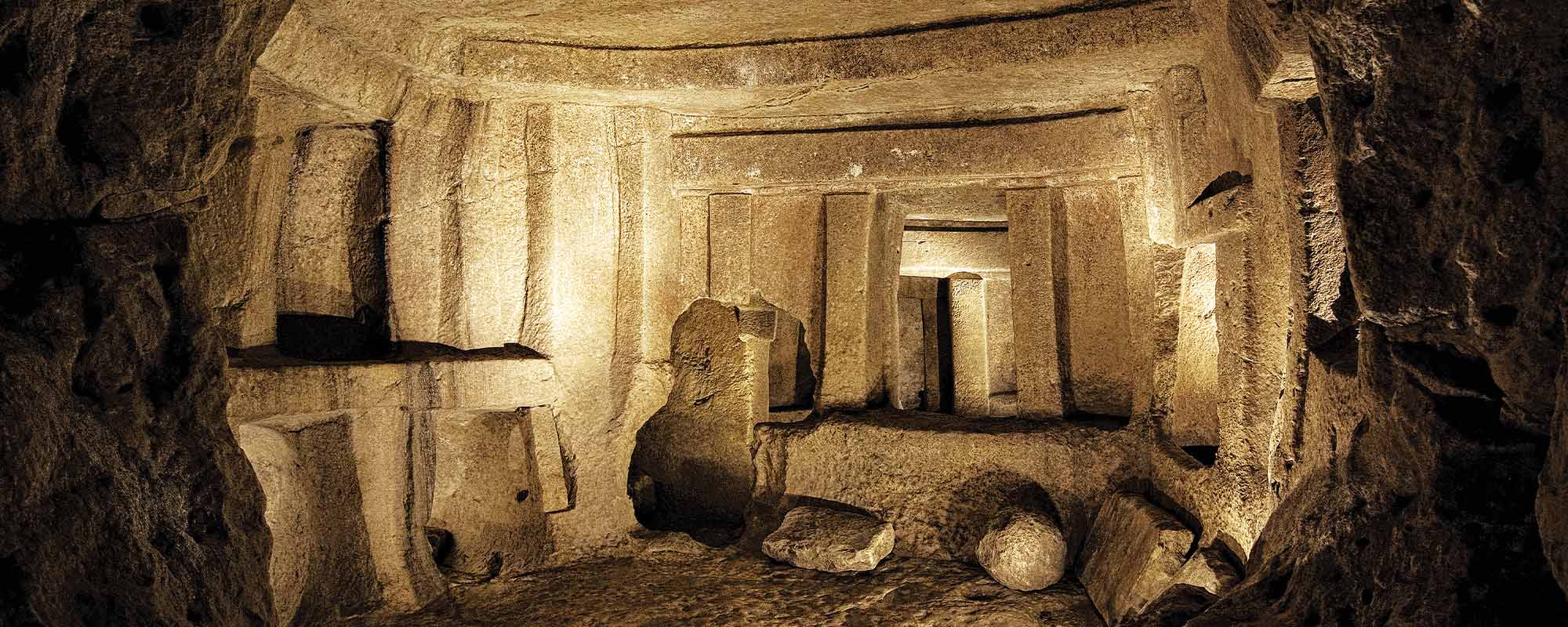
Malta’s Late-Neolithic civilisation erected many magnificent structures, including the Hypogeum of Ħal Saflieni. Using Ħal Saflieni as a case study, new research by Dawn Adrienne Saliba suggests that this structure was likely used for performance rituals and represents an early form of proto-theatre.
Continue readingMalta’s Prehistoric Temples and the People Who Built Them
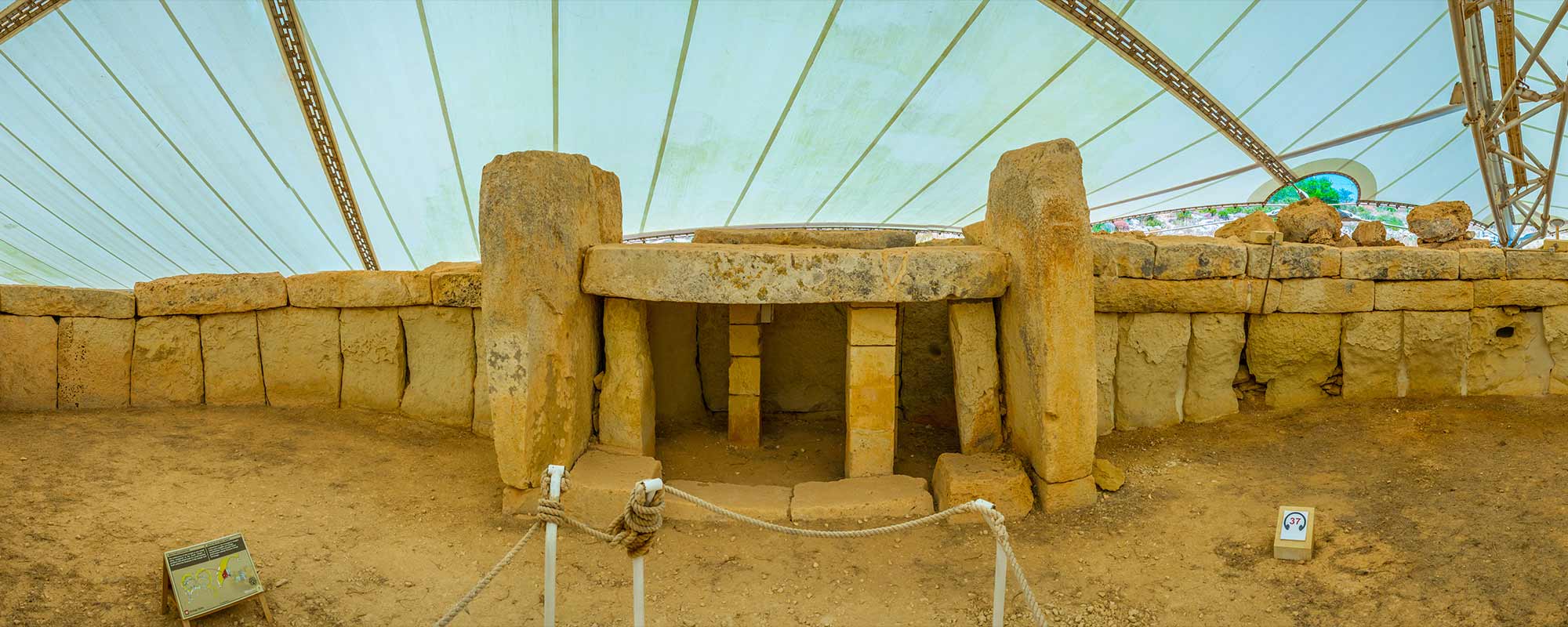
The Maltese megalithic temples were built over 5,000 years ago. To find out how the people that built the temples saw the world, Dr Tore Lomsdalen conducted his PhD project on the worldview and cosmology of the prehistoric Maltese temple builders. He found that the temples were intentionally positioned to be intervisible and oriented towards certain stars that were significant for these ancient people.
Continue readingFiring Up the Past – Unearthing Experimental Archaeology
A university-led project is fabricating Ancient Roman pottery using local raw materials to understand more about Malta’s past
Continue readingPeeling Away the Layers of Time
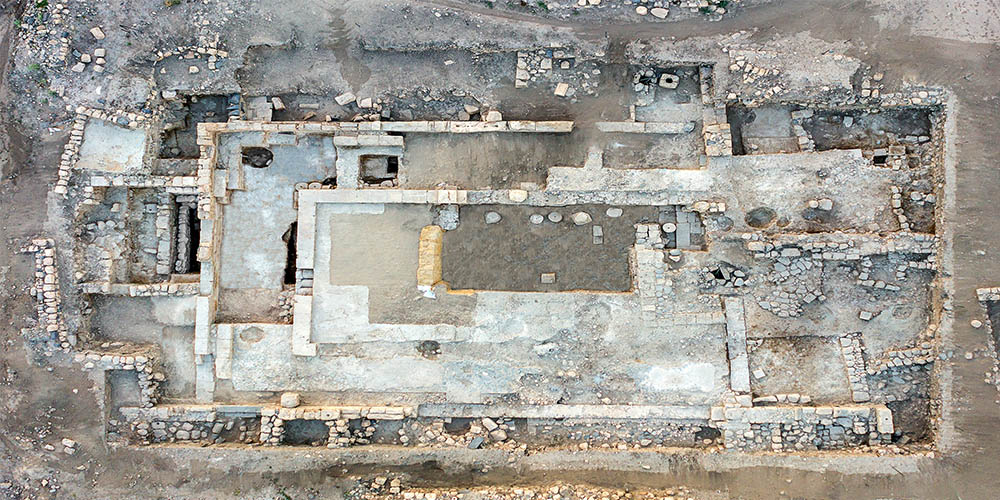
THINK takes a trip to explore research and archaeological work taking place at Borġ in-Nadur, overseen by Heritage Malta, which will see the Neolithic site freed from modern-day debris and accumulated material to show the original prehistoric structure in all its glory.
Continue readingTrading Archaeology & Civilization for Shopping
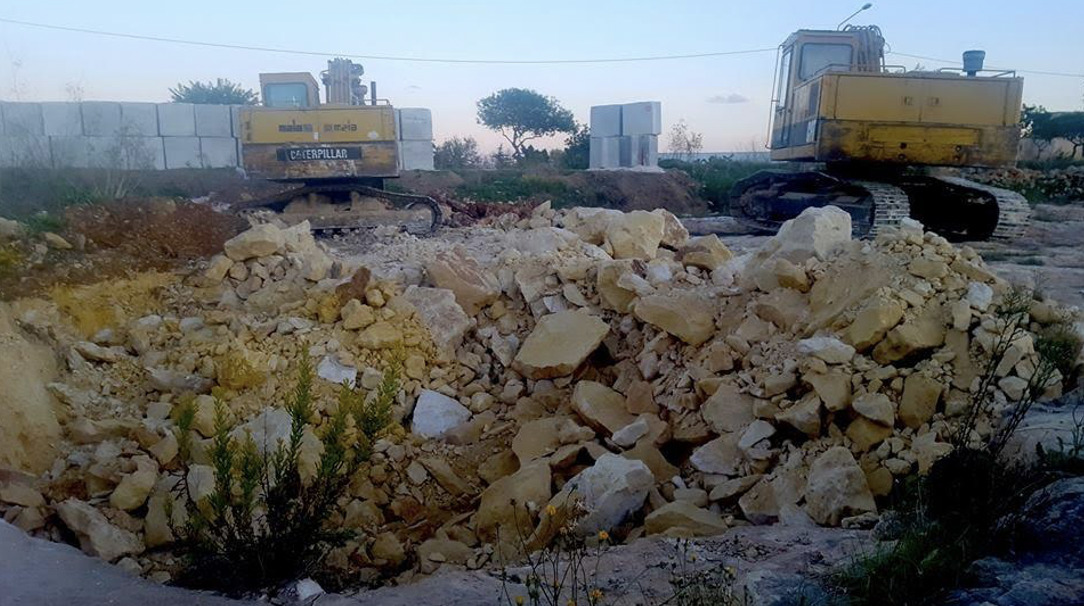
In 1992 the European Convention of the Protection of Archaeological Heritage was signed in Valletta. Ten years later the Maltese Parliament enacted the Cultural Heritage Act. This law was meant to prevent the destruction of Maltese archaeological sites. Sadly, this did not happen. Tal-Qares in Mosta is the latest case of an archaeological site that may soon be lost. Grassroots organisers are now fighting to save it.
Continue readingThe Bible in stone
Excavations of an ancient synagogue at Huqoq, Israel
Buried inside an unassuming hill in Israel’s Lower Galilee is a magnificent ancient synagogue with splendid mosaic panels that have been hidden away for over 1,400 years. Dr Dennis Mizzi writes about the project that is bringing them to light.
Continue readingThe sky’s role in archaeology
In 1994, Czech poet-president Vaclav Havel wrote an article discussing the role of science in helping people understand the world around them. He also noted that in this advance of knowledge, however, something was left behind. ‘We may know immeasurably more about the universe than our ancestors did, and yet it increasingly seems they knew something more essential about it than we do, something that escapes us.’ Almost all traditional cultures looked to the sky for guidance. Cosmology is what gave our ancestors their fundamental sense of where they came from, who they were, and what their role in life was. While arguably incorrect, these ideas created codes of behaviour and bestowed a sense of identity. The cosmology of European prehistoric societies has been studied independently by archaeologists and archaeoastronomers (an interdisciplinary field between archaeology and astronomy). Despite their shared goal of shedding light on our past lives, thoughts, and ideas, the two fields have often failed to merge, mainly due to different approaches. A clear local case is the question of the Maltese megalithic temples.

The Mnajdra South Temple on Malta predates both Stonehenge and the Egyptian pyramids. It is the oldest known site in the world that qualifies as a Neolithic device constructed to cover the path of the rising of the sun throughout a whole year. What is unfortunate is that, so far, archaeologists and archaeoastronomers have studied the site largely in isolation.
Whether the temples were built to visualise the effects of the rising sun as seen today is an open question. But with such specific and repetitive patterning, one cannot deny that the sky was an important element in the builders’ understanding of the world—their cosmology.
With some exceptions, archaeologists have largely ignored, excluded, or underrated the importance of the sky in the cultural interpretation of the material record. When studying ancient communities, chronological dating and economic concerns are often given precedence over the immaterial.
But the fault does not lie solely with disinterested archaeologists. Archaeoastronomy has often been too concerned with collecting astronomical and orientation data, neglecting the wider archaeological record, and ignoring the human element in cosmology.
We need to find a common ground. Both sides need to open themselves up to different professional perspectives and convictions and embrace alternative interpretations and possibilities. Bridging the gap between archaeology and archaeoastronomy will allow us to paint a detailed picture of past societies. And maybe it will shed light on that lost knowledge about the universe and our place in it.
Lomsdalen and Prof. Nicholas Vella are organising an afternoon workshop on Skyscape Archaeology as well as an open symposium on Cosmology in Archaeology. For more information, visit: um.edu.mt/arts/ classics-archaeo/newsandevents
Author: Tore Lomsdalen
Classical Hebrew undying
Classical Hebrew is the Hebrew of the Tanakh, the Jewish Scriptures, the very source of the Christian Old Testament. Its first appearance in the historical record dates back to the 10th century BCE, and like the other semitic languages from which it emerged, it was written from right to left and comprises only consonants. By the turn of the Common or Current Era, its use as a spoken language was quickly being superseded by Aramaic and Greek. A few centuries later it was a linguistic relic, its use limited to liturgical and literary contexts, not so different from the use of Latin much later in the Christian west.
‘Dead’ languages bring up the question of relevance. They are limited in their vocabulary, especially when compared to their contemporaries; the Classical Hebrew lexicon amounts to just about 10,000 words. Today, they could not be used for communication, on official documents, or for most conventional things. However, there is one function ancient languages fulfill in a far superior manner—interpreting ancient texts.
Modern translations cannot quite capture the nuance of ancient texts. Translators can only convey ideas after making countless choices in the understanding and rendering of words, all while being consciously or unconsciously guided by their own ideological leanings. Translations are essentially interpretative exercises. Armed with knowledge of the original language, a reader can identify the original authors’ ideology, emphasis, word order, and tone. All of these features could easily be lost in translation. For example, should the word ‘meshihu’ in Psalm 2:2 be translated as ‘his Messiah’ or ‘his Christ’ or ‘his Anointed One’? A choice needs to be made, and that choice does make a difference.
Archaeologists use the same concept when studying ancient artefacts, as do epigraphists, the specialists who study inscriptions. Understanding the inscribed language on items leads to a clearer, more colourful picture of its context and origins. The Malta Government Scholarship Scheme supported me in carrying out such an epigraphic study for my doctoral research at the University of Oxford. My project dealt specifically with a group of inscribed pottery sherds discovered at Lachish (modern Tell ed-Duweir) in Israel. Combined with an archaeological and contextual reassessment, these inscriptions provided valuable insight into the socio-political history of early 6th-century BCE Judah, including scribal culture and the mastery of the contemporary Hebrew language, as well as military operations and prophetic activity, all of which strike similarities with the Book of Jeremiah.
Studying Classical Hebrew can be a rigorous mental workout that instills an appreciation for detail: an insight useful across innumerable fields. Not only does it provide a solid foundation for Modern Hebrew, but it offers a fresh perspective for those wishing to read biblical texts in a critical manner. After all, the Bible remains an iconic cultural artefact in the western world, vital when discussing not only ideology but even cinema, literature, music, and art.
Ancient languages give a voice to our history and the people who shaped it, all the while providing food for thought for those in the present.
For more information: The Department of Oriental Studies (Faculty of Arts, University of Malta) offers study-units on Classical Hebrew grammar, syntax, and readings at undergraduate level.