Piled higher, dug deeper
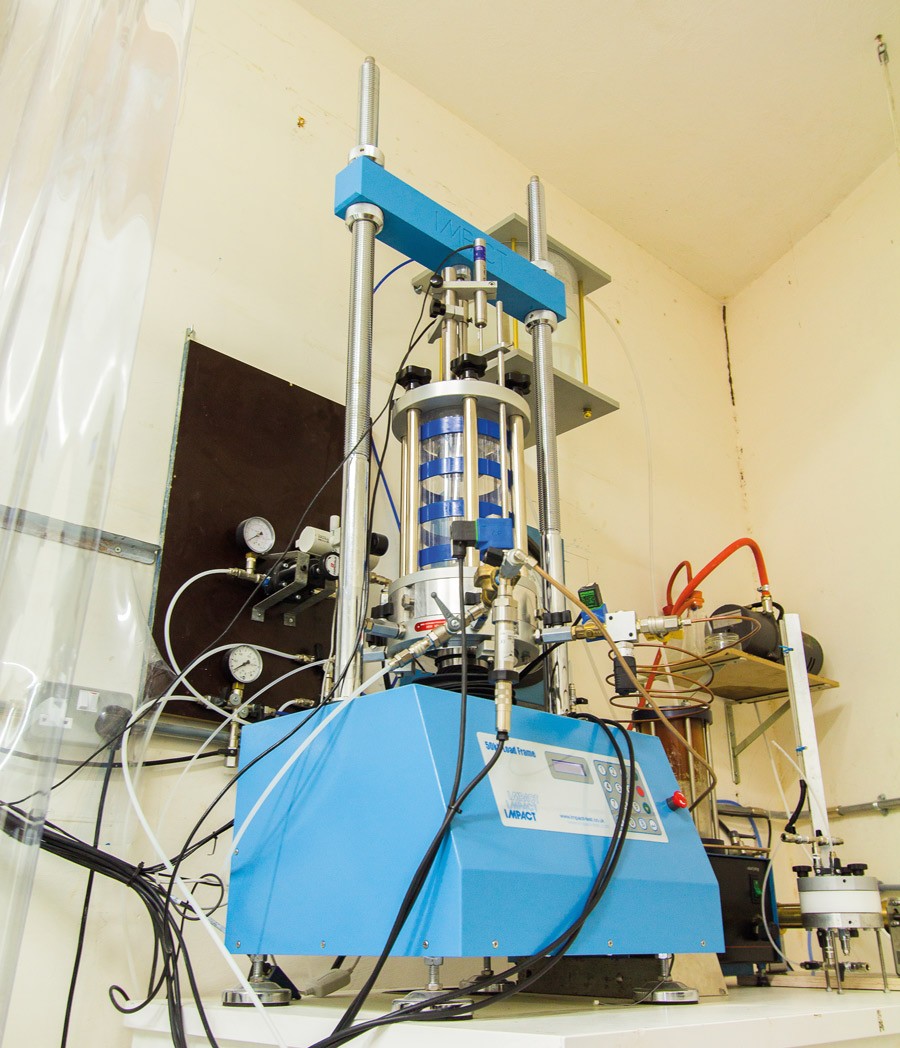
Triaxial testing rigs are used the world over to experiment on ground materials such as soils, rock, or powders. At the University of Malta (UoM), one such rig started being assembled in 2014 using existing equipment at the Faculty for the Built Environment, modernised with the help of the Faculty of Engineering. The rig is now complete, with plans to test rocks typically found in Malta, simulating the stresses created by big excavations and tall towers, steep slopes and deep underground tunnels.
The laboratory is used to investigate the engineering characteristics of weak ground materials such as clay, silt, sand, and weak rock (turbazz in Maltese building terminology). Space and economic pressures are pushing local buildings deeper and taller without the knowledge of how the local rocks can sustain the pressures created. Architects and engineers, now more than ever, are being asked to design excavations and buildings in these weak materials. Abandoning a site for a stronger one is now no longer an option. In-depth understanding of how ground materials behave, therefore, becomes fundamental if dangerous consequences are to be avoided.
| Quick Specs |
|
The equipment is already being used to teach the next generation of architects and engineers. They now have the opportunity to experiment with the local ground materials. They can load them with imagined future buildings or unload them through simulated excavations, all the while observing the real-world effects.
The first real research effort is aimed at understanding what’s going on in Malta’s weak Globigerina limestone, which is currently loaded by heavy buildings. We need to be aware of their internal structure, the water within, how they crush and how long it takes. It’s likely to be a long story, but this is just the beginning.