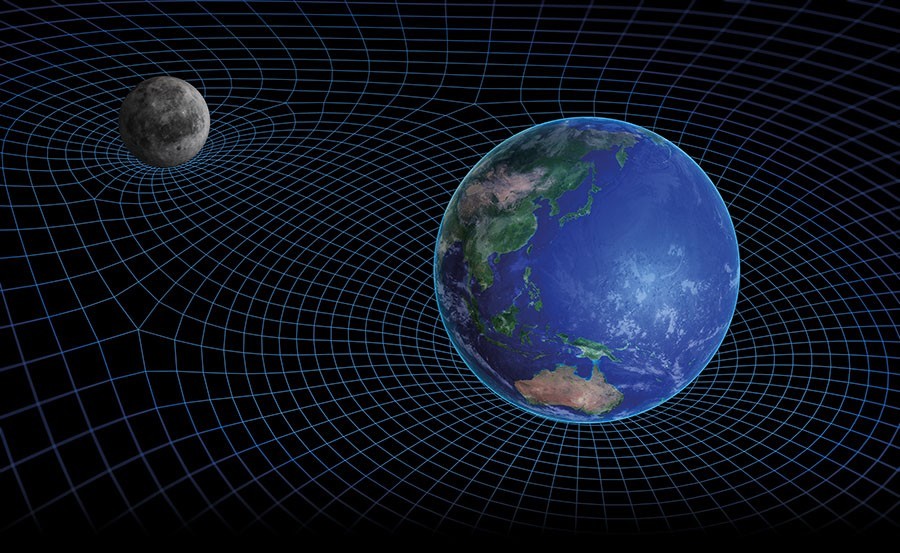
For a primate species clinging to a speck of dust in an incomprehensibly vast universe, curiosity has seen humans discover a great deal about how it all works. However, there are still mysteries that the cosmos is reluctant to relinquish, one of which is gravity. The most accurate theory describing gravitational attraction is general relativity, developed by Albert Einstein in 1915. Unlike Isaac Newton, Einstein did not describe gravity as a force, but rather a manifestation of the curvature of spacetime, thought of as a stretchable and squeezable fabric that is distorted by matter. However, his theory does not fully explain phenomena such as the accelerating expansion of the Universe and inconsistent orbital speeds of stars within galaxies.
So, is Einstein wrong?
More reasonably, the theory is incomplete. To fill in those blanks, Gabriel Farrugia (supervised by Dr Jackson Levi Said, Institute of Space Sciences and Astronomy, University of Malta) is investigating alternative theories of gravity. His focus is on teleparallel gravity, in which spacetime is twisted rather than curved. This is a new description that can be used to construct more general theories and models. As part of his research, Farrugia investigated whether a particular extension of teleparallelism can describe the evolution of large-scale structures like galaxy formation with current observational data.

In this model, the effect of gravity is not only dependent on the torsion being produced but on the type of material gravitating. Although it has been concluded that the model is not sound unless special circumstances are considered, this is not a negative result. It serves to restrict the number of possible valid theories and ultimately help find the true theoretical description of gravitation. The phenomena these theories try to explain are unlikely to directly affect our lives. Yet, understanding them will not only broaden our repertoire of knowledge, but helps us develop better technologies.
Thanks to Newton, humanity was able to determine the periods of planets around the Sun that helped build the first rockets and satellites. Thanks to Einstein, the Global Positioning System (GPS) became a reality. Given the importance of these technologies to our current lifestyles, who knows what technological revolutions such research will make possible?



Comments are closed for this article!