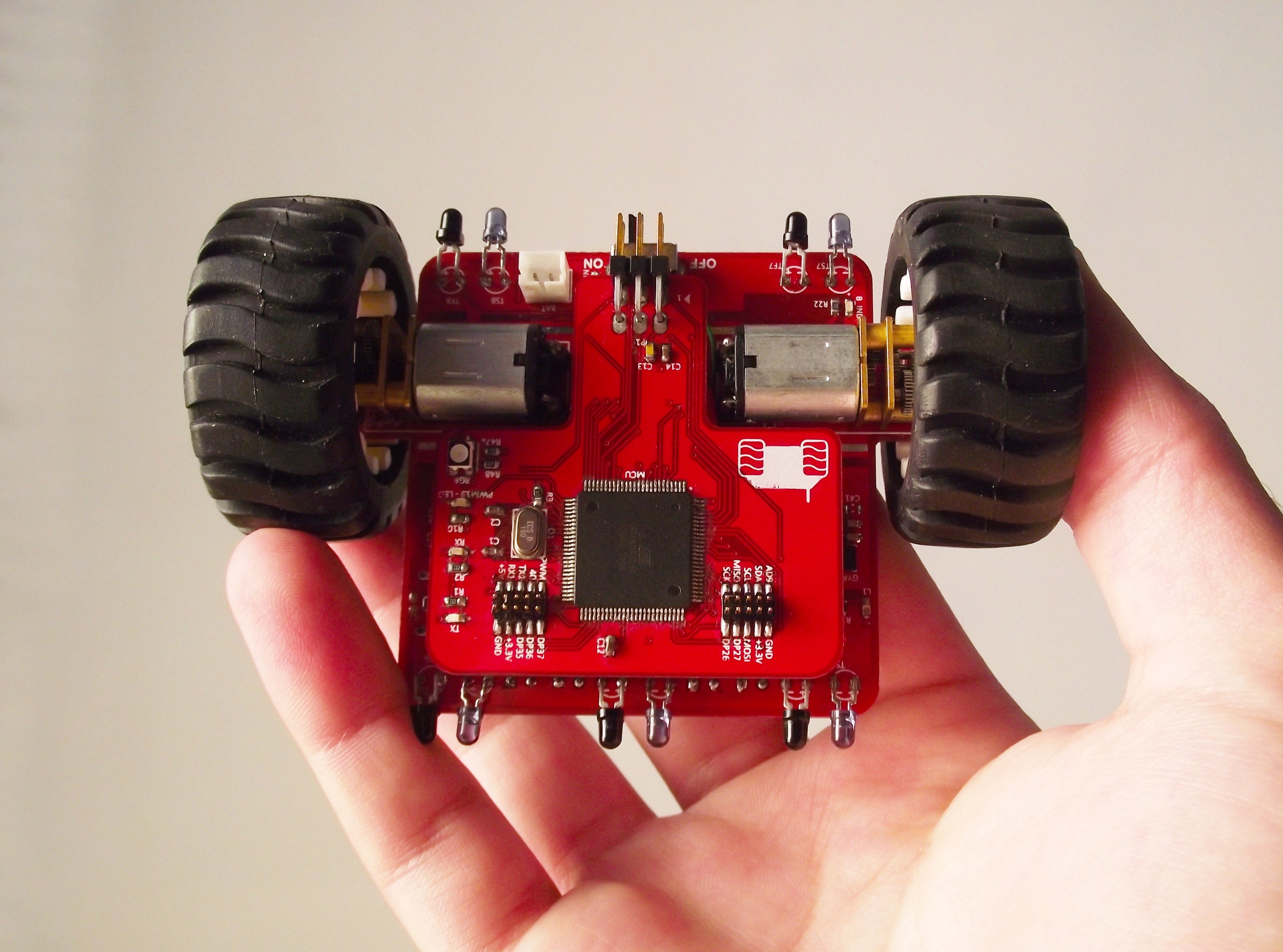
Reuben Ferrante, a University of Malta Engineering graduate and founder of eeRoot, has developed a small robot called eeMod. eeMods are built from only two modules stacked on top of each other. The bottom module is a ‘sensor hub’ that can sense the environment around it. It does so through connections (wifi, bluetooth, USB, microSD card slot), several sensors (gyroscope, accelerometer, light sensors), and a bit more wizardry. The second module is the controller, or brain. Its programmable controller is entirely compatible with the Arduino platform—a standard used worldwide. A set of wheels let’s the eeMod zip around.
Because the robot’s brain is empty by default, it can be hooked up to a computer to upload data. eeMods understand complex instructions and can utilise their senses to act accordingly. Users can start programming by using a very simple Arduino compatible drag and drop interface, and later make the transition to writing their own code. Having all that technology in one sleek package is one of the their unique selling points. Although eeMods were originally designed to streamline the scientific workflow in robotics, it is receiving a lot of attention from educational institutions. The robot’s simplicity allows it to be uses in schools giving children early insight into robotics. Ferrante has received multiple requests to provide a syllabus paired to the eeMods and tailored to Malta’s educational system.
Sphero is another miniature classroom robot, but looks very different from an eeMod. The company SPRK provides a near indestructible ball that can move around via various motors at its core. Recently the developers made it possible to programme Sphero through a smartphone app. For some quick fun the ball can also be remote controlled using the same app. It can move across all kinds of surfaces, and even through water—the perfect classroom bot.
The robots approach education from different angles and target different age groups. eeMods are the perfect device to delve into the technology behind robotics and learn programming algorithms early, while Sphero is a nice toy to play around with, enabling even technophobe people to experience the miracle that robots are.
With an increasing presence in everyday life robots are here to stay, in one form or the other. Allowing children to get familiar with the technology early helps teach lifelong skills and inspire them for the rest of their life.
For more information visit the official eeRoots website.
This article first appeared in ‘Sounds of Science’ in the Times of Malta, May 22 2016.




Comments are closed for this article!