
Drawing can be defined as the active exploration of an individual’s mental imagery. John Berger described it as ‘an autobiographical record of one’s discovery of an event—seen, remembered, or imagined.’
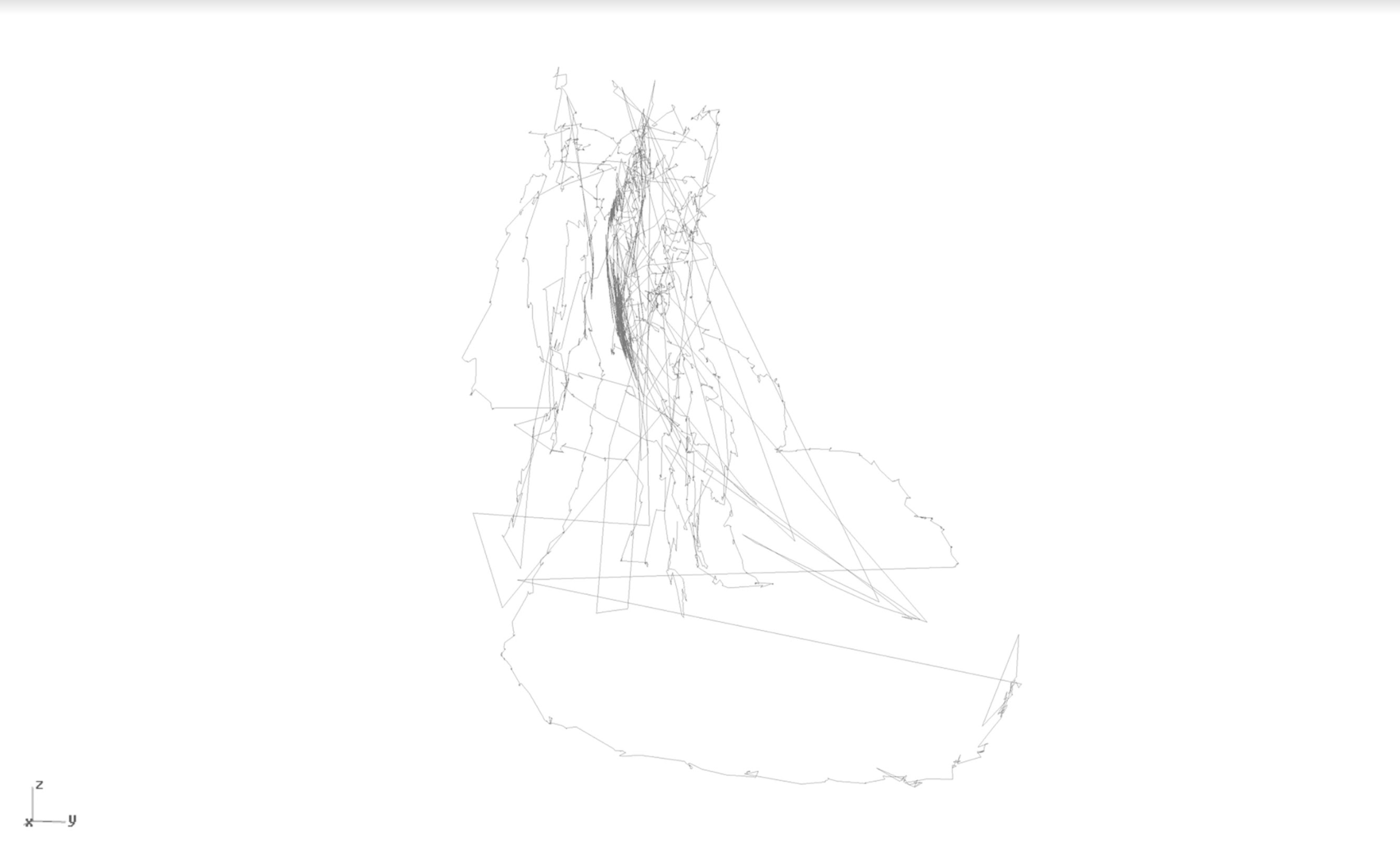
The initial hunch for my research revolved around the idea of drawing with one’s eyes instead of hands by using an eye-tracker.
The approach intrigued me for three reasons. It allowed me to explore the notion that an artist’s skills are in his tools—his hands. The eye-tracker-based technique ‘levelled the playing field’ between artist and non-practitioner by removing hands from the equation. Secondly, through eye-drawing practice, I could also notice a shift in the drawing methods used. Normal drawing involves hand-eye coordination and a degree of intuitive eye movements. In ‘eye-drawing’, these movements have to be suppressed into following contours along the observed worldview, while also restraining the impulse to refer to the accustomed curvilinear hand motions. All this feeds into the fact that eye-drawing cannot be regarded through the same approach as ‘normal’ drawing. Eye-drawn objects have a direct representation tied to their place and time of execution and acquire a technological aesthetic.
I explored these concepts in several experiments. I ran communal ‘life’ eye-drawing classes with first year students reading for an MFA (Faculty of Media and Knowledge Sciences, University of Malta [UM]). Their resulting visuals were surprisingly individualistic, highlighting their characters, a quality I observed to be constant throughout all eye-drawings.
Using an eye-tracker to draw led to some exciting possibilities. I tested a preliminary algorithm, developed by my colleague Neil Mizzi, (Faculty of ICT, UM) that ‘corrected’ an eye-drawing by comparing it to a real-world picture. The technique could be applied in future eye-drawing devices designed to help physically impaired individuals to draw from real-world images using just their eyes.
It can be argued that art is a subjective experience, both in its creation and perception. Eye-drawing can exploit this subjectivity revealing ‘signature’ gestures through a new way of looking.
This research was carried out as part of a Masters by research at the Department of Digital Arts, Faculty of Media and Knowledge Sciences, University of Malta (UM).



Comments are closed for this article!