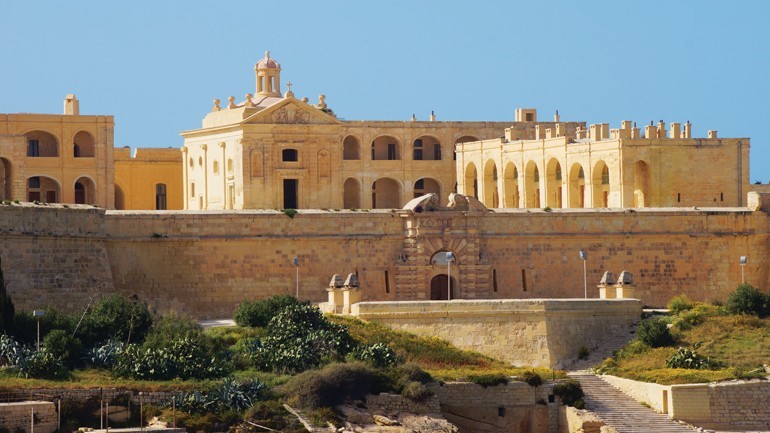
Malta has three UNESCO world heritage sites which need constant conservation. Generally, it is better to preserve the original building material than replace it. The conservation method called consolidation can glue deteriorating stone material to the underlying healthy stone maintaining it, but few consolidants have been tested on local Globigerina limestone. Sophie Briffa (supervised by Daniel Vella) tested a new set of consolidants which are stronger than other compounds but affected the colour of the stone. She applied five different conditions on the stone. The first three were novel treatments. They were based on a hybrid silane (tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) and 3-(glycidoxypropyl)trimethoxysilane (GPTMS)) but one had nanoparticles, one had modified nanoparticles, and the other lacked them. The fourth was a simple laboratory-prepared TEOS silane. The fifth was untreated limestone samples for comparison.
The treatments successfully penetrated the stone’s surface. Microscopy coupled with other techniques including mercury intrusion porosimetry carried out in Cadiz, Spain, confirmed this infiltration and the stone’s physical qualities: strength, drilling resistance, and so on. Half of the treated stones underwent accelerated weathering. The consolidants with nanoparticles or modified nanoparticles were stronger than the other treatments. They also maintained the original surface colour and improved the stones’ ability to absorb water. On the other hand, they were less resistant to salt crystallisation that can damage the stone making it brittle.
The best consolidant for Maltese stone has not yet been found. Ideally, it should have a good penetration and good weathering properties that preserve the stone’s appearance. It should allow ‘breathability’ and be reversible. Current stone consolidation techniques are irreversible since they permanently introduce new material into the stone. These are only acceptable since consolidation is a last attempt to save the stone before complete replacement.
French writer Victor Hugo summed up the importance of this research when he said, ‘Whatever may be the future of architecture, in whatever manner our young architects may one day solve the question of their art, let us, while waiting for new monuments, preserve the ancient monuments. Let us… inspire the nation with a love for national architecture’.
This research was performed as part of an M.Sc. in Mechanical Engineering at the Faculty of Engineering. The research was funded by the Strategic Educational Pathways Scholarship (Malta).




Comments are closed for this article!