The economies of small states are vulnerable. Their size and open nature leaves them exposed to economic shocks. William Gatt (supervised by Dr Gordon Cordina) from the University of Malta and Central Bank of Malta modeled an economy to study the effects of government policies in limiting economic turmoil. The researcher used a Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium (DSGE) model of a small, open economy to simulate an economy similar to Malta. The model could study an economy over time, determine its reaction to random shocks, and the effect of changes in policy. Mr Gatt compared a government policy which directly shored up ‘at risk’ households to another policy with which government boosted economic activity by directly buying goods from the market. Direct transfers to households accelerated a faster economic recovery after drops in foreign demand.
Further studies showed that government intervention is more beneficial when more ‘at risk’ households exist. The downside to this policy is a requirement of a large economic surplus. Government would need to save when the economy is strong to buffer in times of distress. In this light, the role of government is as a saver, meaning that it should ensure precautionary savings adjusting policy targets for a budget surplus. 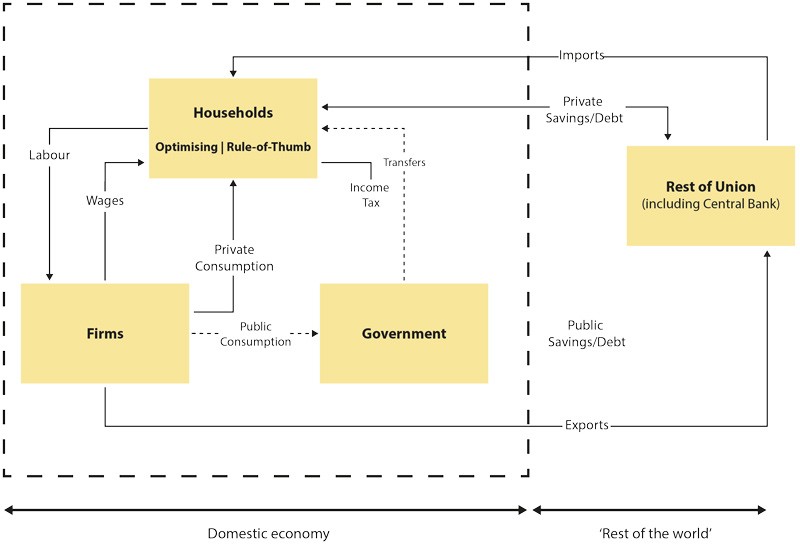
This research was undertaken as part of a Master of Arts in Economics from the Faculty of Economics, Management and Accountancy. Opinions expressed are those of the author and not necessarily those of the Central Bank of Malta.




Comments are closed for this article!