
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a disease that affects over 250 million people worldwide. Many in Malta suffer from the disease because of our high carbohydrate diet and lack of physical activity. Type 2 diabetes arises when levels of the sugar glucose remain very high in the blood. Testing normally involves frequent finger pricks to determine blood sugar levels, or otherwise a patient can take a sugary drink followed by regular urine/blood testing over 2 or more hours.
Alexandra Fiott (supervised by Prof. A. Felice) studied whether the absolute HbA1c levels (the haemoglobin fraction with sugar attached multiplied by the haemoglobin concentration) would provide a better method to describe the link between one’s genetics and diabetic condition. She attempted to reduce the frequency of the testing needed while using a relatively non-invasive test — the withdrawing of one tube of blood, while investigating the genetics of diabetes.
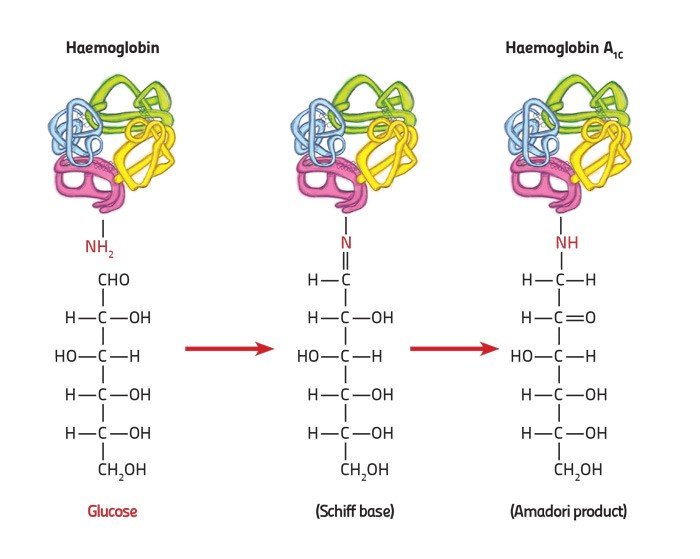
Haemoglobin (Hb) transports oxygen throughout the blood through red blood cells. The HbA1c forms when glucose binds to haemoglobin. This can be used as an indirect measure of average blood sugar concentrations. Measuring HbA1c levels is rapid, but unfortunately the results are influenced by factors that affect red blood cells. With around 5% of Maltese having red blood cell disorders, an alternative measurement would help reduce inaccurate results and unnecessary worry for patients. The absolute HbA1c was used for this study.
The genetics and blood profile of five different patient groups were determined using genetic and biochemical methods: adults with a normal blood profile, anaemics, beta-thalassaemics, pregnant women, and type 2 diabetics (on limited treatment). Statistical analysis did not reveal an improved link, but the absolute HbA1c did help distinguish between the different patient groups.
To improve the reliability of these results, a separate set of experiments was carried out to see whether a known Maltese variation in haemoglobin, with a prevalence of around 1.8% in the Maltese population, has an effect on the amount of sugar that binds to the haemoglobin. This variant was found not to influence the blood glucose levels and therefore the HbA1c.
Taken together these results showed that the absolute HbA1c does not improve the link between the genetics and blood profile of the patients. However, it could distinguish between different groups of patients.
This research was performed as part of an M.Sc. (Melit.) in Biomedical Sciences at the Faculty of Medicine and Surgery at the University of Malta.




Comments are closed for this article!