| Tech Specs |

Sensors: Trillium 120PA/Trillium Compact Technology : 3 symmetric triaxial sensors with force feedback Bandwidth: 8mHz to 150Hz Weight: 7.2kg/1.2kg Height: 20cm/10cm Power consumption: 600mW/160mW Data Loggers: Centaur 24-bit ADC, Internet-enabled |
The earth’s surface is never still. And that is why over the past three years the Seismic Monitoring and Research Group (Faculty of Science, Department of Geosciences), has been placing its ears more firmly to the ground, listening to the smallest vibrations of our Earth.
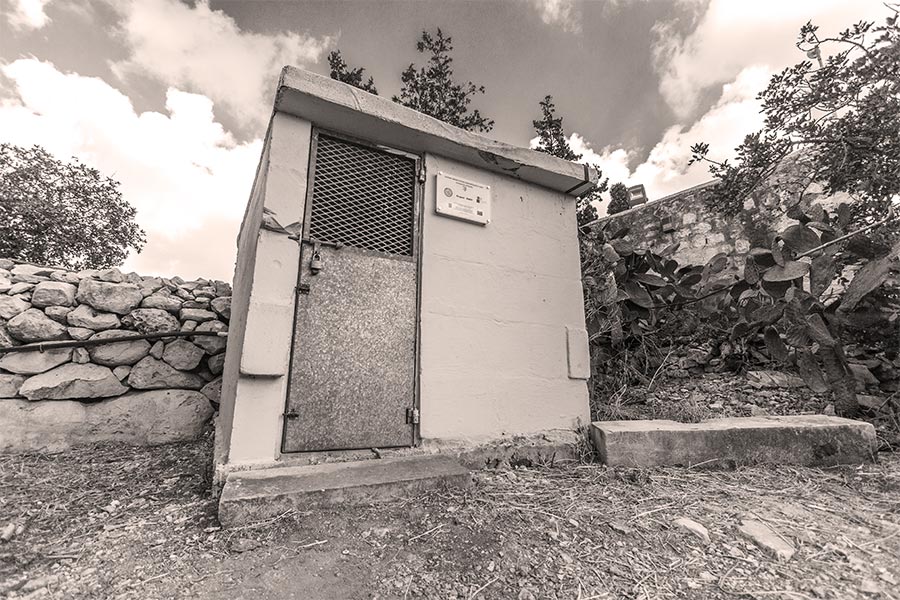
Since 1995 the Malta Seismic Network has grown from a single seismic station at Wied Dalam to a network of six broadband instruments all over the Maltese Islands.
Stations are installed in several locations. The sensitivity of the instruments means that they need to be homed in places where human interference is minimal. Church crypts and underground tunnels are perfect. Being broadband instruments, they can detect very slow vibrations from frequencies less than a millihertz (the whole Earth’s normal mode frequencies), to tens of hertz (ground motion from anthropogenic noise and near earthquakes).
The network can record close ‘microearthquakes’ with equal clarity to large earthquakes from all over the globe. These massive quakes send seismic waves travelling through the planet’s interior at several kilometres per second. All of this data is transmitted to a University of Malta server, which distributes the information to data centres worldwide.
But what is the advantage of having so many stations in such a small area? Firstly, researchers can gather valuable information and share it with the seismological community to build more detailed models of the Earth’s interior. Secondly, an immediate advantage is the enhanced detection and analysis of smaller and smaller earthquakes from all sides of the island, leading to a deeper insight of active faults. Thirdly, the network gives precious information on the proper es and structure of the rocks of Malta. More accurate information about our islands’ composition and behaviour will help make Malta earthquake-ready.





Comments are closed for this article!